Trouble for Tesla: Why Consumer Reports Says Its Model S Was ‘Undriveable’

Consumer Reports in 2013 gave the Telsa Model S the highest rating of any vehicle in its history. This year’s review did not go as well for Elon Musk’s company.
The venerable magazine had to delay testing of the company’s newest model because its drivers couldn’t open the doors on the $127,000 sedan, temporarily making the car “undriveable.”
The door handles on the Model S P85 retract automatically and lay flush against the vehicle when they are not in use. Once the vehicle receives a signal from the key fob, the handles move to allow people to grip them. Unfortunately, the door handles stopped working after Consumer Reports testers had the vehicle for 27 days and had driven just over 2,300 miles.
That malfunction caused other problems, the magazine says: “[S]ignificantly, the car wouldn't stay in Drive, perhaps misinterpreting that the door was open due to the issue with the door handle.”
Consumer Reports’ troubles aren’t unique. The non-profit’s car reliability survey found that the Model S has had a far higher than average number of problems with doors, locks and latches, according to the organization’s website.
The testing experience wasn’t all bad, though, because the automaker’s customer service is top notch. A technician was sent to the Consumer Reports Auto Test Center the morning after the problem was reported and quickly diagnosed the problem.
“Our car needed a new door-handle control module — the part inside the door itself that includes the electronic sensors and motors to operate the door handle and open the door,” Consumer Reports says. “The whole repair took about two hours and was covered under the warranty.”
Eric Lyman, vice president of industry insights at TrueCar, told The Fiscal Times that the speed in which Tesla addressed that issue will earn it more kudos from customers who have seen carmakers drag their feet in making needed repairs. The door handle issue isn’t a big deal, he said.
“Telsa is still a relatively new automaker,” he said. “The reality is that we see this kind of thing happen all of the time. This is pretty normal in the course of business in the auto industry.”
The timing of the mishap comes as Telsa is struggling to repair its credibility with Wall Street after the electric vehicle maker’s disappointing earnings performance. Bloomberg News reported last week that the Palo Alto, Calif.-based company might have to raise money because of what one analyst described as its “eye watering” cash burn rate, or else it might run out of money in the next three quarters.
The electric vehicle maker also is facing increased competition from more established rivals. General Motors (GM), for instance, recently unveiled a Chevrolet Bolt concept car that is set to hit the market in 2017 with a projected price of about $30,000 and a battery range of 200 miles. The next generation Nissan Leaf, another electric vehicle, will hit the market at about the same time.
For now, Tesla’s biggest challenge may in convincing consumers to buy electric vehicles while oil remains cheap.
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
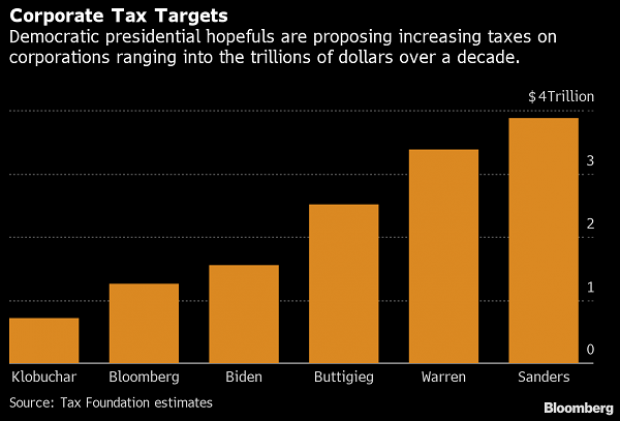
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
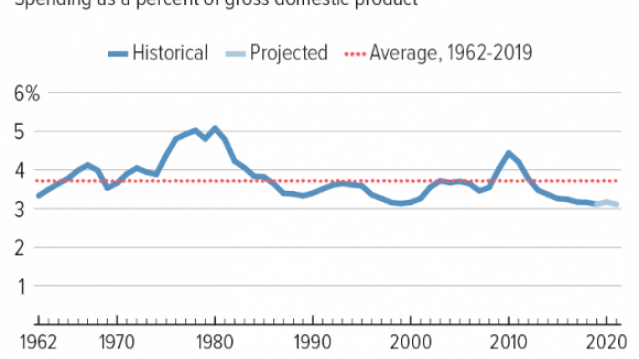
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
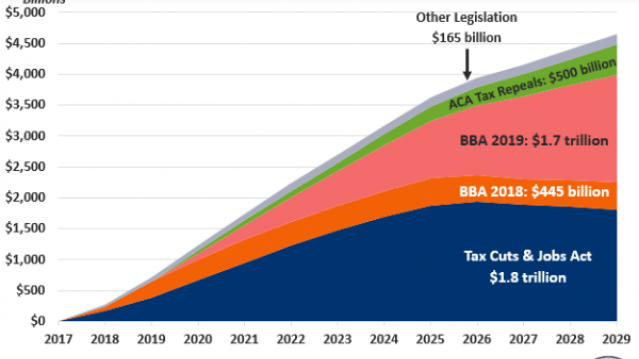
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
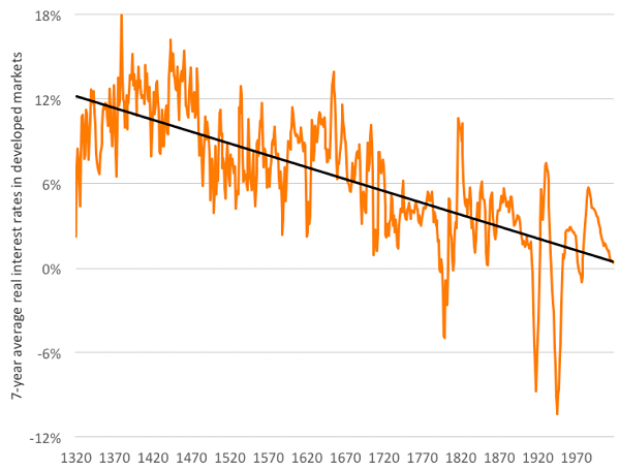
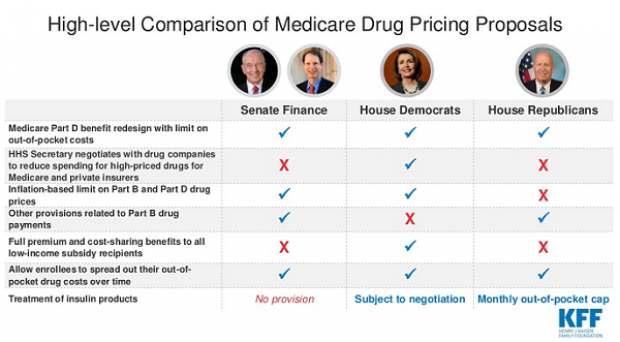
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.