Get Ready for Your 'Daily Glitch'—The NYSE, WSJ and United Were Just the Beginning

“Glitch” is clearly the word of the moment, after a series of pesky little technical problems forced United Airlines to ground flights, halted New York Stock Exchange trading and took down The Wall Street Journal website homepage all on the same day. If that wasn’t enough technical trouble, Seattle’s 911 system went down briefly. And a couple of NASA spacecraft also suffered “glitches” in recent days.
We deal routinely with glitches these days — a Wi-Fi connection goes down, an app freezes, a plug-in (usually Shockwave) stops responding, an email doesn’t load properly — which may help explain why, aside from lots of grumbling from delayed airline passengers, the reaction to Wednesday’s glitches was rather muted. The NYSE problems were reportedly caused by a “configuration issue” after a software update and United blamed its problem on “degraded network connectivity.” We see those issues every day, just not on as large a scale.
But that’s the problem.
At the risk of sounding like a high school term paper, let us note that the Merriam-Webster definition of glitch is “an unexpected and usually minor problem; especially: a minor problem with a machine or device (such as a computer).” The full definition describes it as a minor problem that causes a temporary setback.
Sure, Wednesday’s setbacks were all temporary. The Wall Street Journal site came back up quickly. Seattle’s 911 service was restored. Action on the NYSE itself was stopped for nearly four hours, but even then traders were still able to buy and sell NYSE-listed stocks on other exchanges. United grounded about 3,500 flights, which meant some people missed a wedding or a crucial business meeting. That will take time to sort out, but it will get sorted out.
In aggregate, though, the problems add up — and the word “glitch” only minimizes what can be much bigger, more serious issues..
Stock exchanges have suffered from a series of stoppage-causing glitches in recent years, pointing to the value of having trading spread across numerous exchanges. United’s tech breakdown “marked the latest in a series of airline delays and cancellations in the last few years that experts blame on massive, interconnected computer systems that lack sufficient staff and financial backing,” the Los Angeles Times reports. Just ask any of the roughly 400,000 United passengers whose travel plans were messed up if this was a little glitch. Or maybe check with the engineers who had to troubleshoot and rebuild the HealthCare.gov site after its glitch-laden launch.
It may be some relief that these latest outages weren’t the result of external attacks, but as sociologist Zeynep Tufecki, an assistant professor at the School of Information at the University of North Carolina, writes at The Message, “The big problem we face isn’t coordinated cyber-terrorism, it’s that software sucks. Software sucks for many reasons, all of which go deep, are entangled, and expensive to fix.”
These foul-ups are now mundane, and to some extent they may be inevitable as we rely more and more on complicated computer systems in every aspect of our lives. That’s the real issue, and it’s a lot bigger than a glitch.
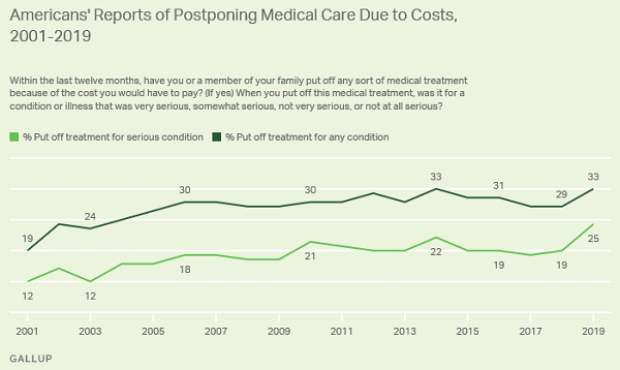
Increasing Number of Americans Delay Medical Care Due to Cost: Gallup

From Gallup: “A record 25% of Americans say they or a family member put off treatment for a serious medical condition in the past year because of the cost, up from 19% a year ago and the highest in Gallup's trend. Another 8% said they or a family member put off treatment for a less serious condition, bringing the total percentage of households delaying care due to costs to 33%, tying the high from 2014.”
Number of the Day: $213 Million

That’s how much the private debt collection program at the IRS collected in the 2019 fiscal year. In the black for the second year in a row, the program cleared nearly $148 million after commissions and administrative costs.
The controversial program, which empowers private firms to go after delinquent taxpayers, began in 2004 and ran for five years before the IRS ended it following a review. It was restarted in 2015 and ran at a loss for the next two years.
Senate Finance Chairman Chuck Grassley (R-IA), who played a central role in establishing the program, said Monday that the net proceeds are currently being used to hire 200 special compliance personnel at the IRS.
US Deficit Up 12% to $342 Billion for First Two Months of Fiscal 2020: CBO

The federal budget deficit for October and November was $342 billion, up $36 billion or 12% from the same period last year, the Congressional Budget Office estimated on Monday. Revenues were up 3% while outlays rose by 6%, CBO said.
Hospitals Sue to Protect Secret Prices

As expected, groups representing hospitals sued the Trump administration Wednesday to stop a new regulation would require them to make public the prices for services they negotiate with insurers. Claiming the rule “is unlawful, several times over,” the industry groups, which include the American Hospital Association, say the rule violates their First Amendment rights, among other issues.
"The burden of compliance with the rule is enormous, and way out of line with any projected benefits associated with the rule," the suit says. In response, a spokesperson for the Department of Health and Human Services said that hospitals “should be ashamed that they aren’t willing to provide American patients the cost of a service before they purchase it.”
See the lawsuit here, or read more at The New York Times.
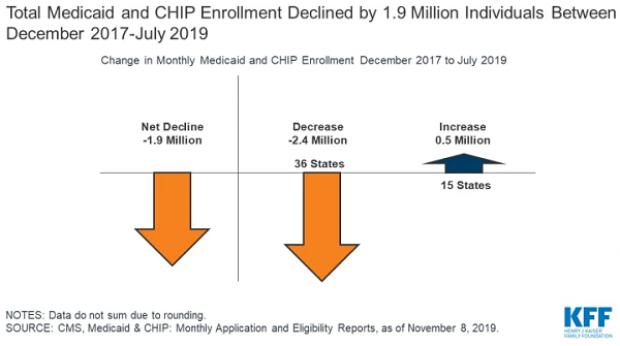
A Decline in Medicaid and CHIP Enrollment
Between December 2017 and July 2019, enrollment in Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) fell by 1.9 million, or 2.6%. The Kaiser Family Foundation provided an analysis of that drop Monday, saying that while some of it was likely caused by enrollees finding jobs that offer private insurance, a significant portion is related to enrollees losing health insurance of any kind. “Experiences in some states suggest that some eligible people may be losing coverage due to barriers maintaining coverage associated with renewal processes and periodic eligibility checks,” Kaiser said.