Donald Trump Isn’t as Rich as He Says…but He’s Still Pretty Rich

“I’m really rich,” Donald Trump boasted last month when he announced he was running for president. A new analysis by Bloomberg confirms that claim, but finds that the real estate mogul and presidential candidate is worth about $7 billion less than he claims.
When he announced his presidential bid, Trump touted a net worth of about $8.7 billion, a figure that soon ballooned to $10 billion. But Bloomberg calculates his wealth closer to around $2.9 billion. The Bloomberg Billionaires Index, a daily ranking of the world’s biggest fortunes, arrived at the value using both prior-known information and a 92-page personal disclosure form that Trump filed with the Federal Election Commission.
Related: 7 Revelations from Donald Trump’s Financial Disclosure
The federal form that all presidential candidates are required to submit asks only for broad ranges in asset values, not specific sums. Anything above $50 million in value is lumped together in one category, which in Trump’s case left plenty of room for questions about just how valuable some of his assets are. The federal report also doesn’t require candidates to list personal property like art, clothing or real estate that’s for his own use.
The Bloomberg analysis went into much more depth, using figures such as purchase dates, square footage, rental rates and more.
The disclosure form revealed that most of Trump’s fortune comes from real estate holdings, such as the Trump Doral resorts in Florida and Trump Tower on Fifth Avenue in New York City. Other lucrative properties include premier golf courses in the U.S., Ireland and Scotland.
Related: Donald Trump Just Showed Why His Campaign Is Doomed
Trump had valued his golf and resort properties at $2 billion. Bloomberg, using price-to-sales ratios for similar properties, put the value at a combined $570 million.
The Bloomberg methodology also doesn’t put much value in the Trump brand, counting only the cash being held as part of licensing or other business deals. “Trump’s own estimations,” Bloomberg noted, “include much higher values for his brand.”
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- Huckabee Trounces Trump in the Shameless Shock Game
- You’re Richer Than You Think. Really.
- 15 Facts You Didn’t Know About Donald Trump
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
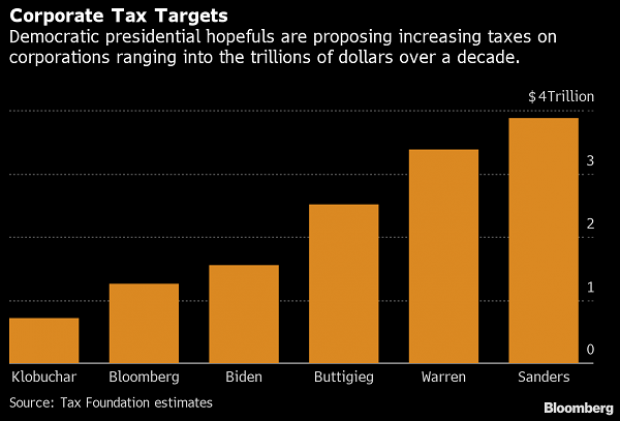
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
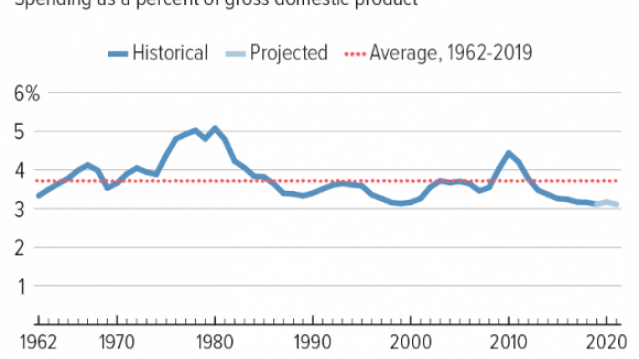
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
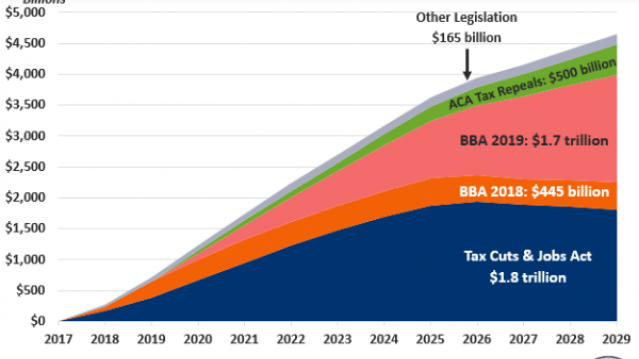
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
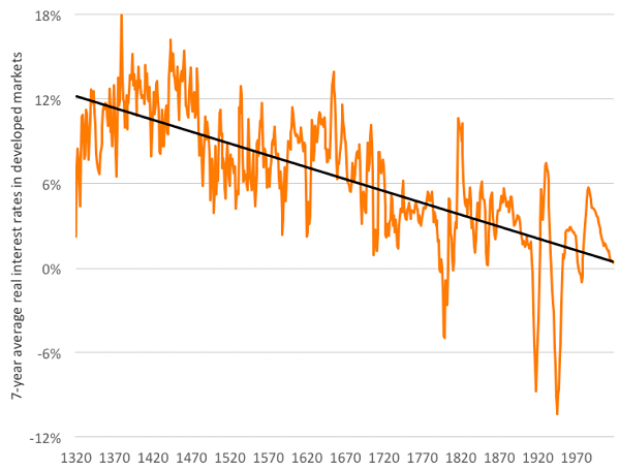
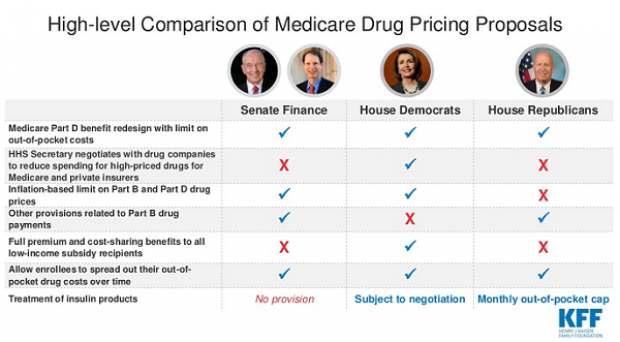
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.