Obama Faces Widespread Public Distrust on Iran Deal
President Obama will try to drum up support for the U.S.-Iran nuclear deal Wednesday afternoon at a news conference. But with widespread public disdain and distrust of Iran, Obama may have trouble convincing Americans of the wisdom of dealing with a long-time arch enemy in the Middle East.
The U.S. and Iran on Tuesday announced an agreement that would potentially block Iran’s development of a nuclear weapon for at least a decade while lifting international economic sanctions against Tehran. However, a new AP-GfK poll that was conducted just ahead of the announcement found that Americans only narrowly back diplomatic relations with the hardline Islamic government, and many want to see the sanctions kept in place.
Related: The 8 Most Important Things to Know About the Iran Nuclear Deal
Just 51 percent of those interviewed said the U.S. should have diplomatic relations with Iran while 45 percent said it shouldn’t. At the same time, 77 percent of those interviewed said the harsh U.S. and international economic sanctions against Iran should be preserved at current levels or even increased.
Only 12 percent of those interviewed thought sanctions should be decreased and seven percent said they should be eliminated altogether.
The public’s wariness and distrust of dating back to the 1979 Iranian revolution and U.S. hostage crisis matches the reception the nuclear agreement has received on Capitol Hill where most Republicans and some Democrats say they fear Obama has conceded too much to a country that has fomented terrorist activities throughout the Middle East and has repeatedly vowed to destroy Israel.
Fifty-six percent of Americans consider Iran to be an enemy, according to the poll conducted last Thursday through Monday, while an additional 31 percent consider Iran to be unfriendly but not an enemy. More than 70 percent of Republicans, half of all independents and 45 percent of Democrats described Iran as the enemy.
Related: Clinton Cautious in Her Praise of a Nuclear Deal She Helped to Orchestrate
Before the agreement was announced, six in ten Americans said they disapproved of Obama's handling of the U.S. relationship with Iran, while just over a third approved.
Obama is likely to prevail in pushing the nuclear non-proliferation agreement through Congress over the next two months, despite near-unanimous opposition from Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell, House Speaker John Boehner and other leaders and rank and file Republicans. Still, he will need to hold in place at least 34 of the 46 Democrats in the Senate to create a veto-proof firewall in the event Republicans push through a resolution of disapproval of the nuclear deal.
That means that Obama cannot afford any more than 12 Democratic defections to keep the agreement alive. Yesterday, Obama and Vice President Joe Biden began working the phones to shore up support on Capitol Hill, and the president will continue that effort during this afternoon’s White House press conference.
During an interview yesterday with Tom Friedman of The New York Times, Obama stressed that the deal prevented a pathway for Iran to develop a nuclear weapon while making it clear he shared Americans’ distrust of the Iranian government and had limited expectations of improved relations down the road.
Related: Iran Agrees to Limit Nuclear Weapon in Historic Deal
When announcing the deal yesterday, Obama said, “This deal is not built on trust -- it's built on verification…. We will, for the first time, be in a position to verify that Iran is meeting all of these commitments. International nuclear inspectors will have access to Iran's nuclear program -- where necessary, when necessary. This is the most comprehensive and intrusive verification regime that we have ever negotiated. If Iran tries to divert raw materials to covert facilities, inspectors will be able to access any suspicious locations.”
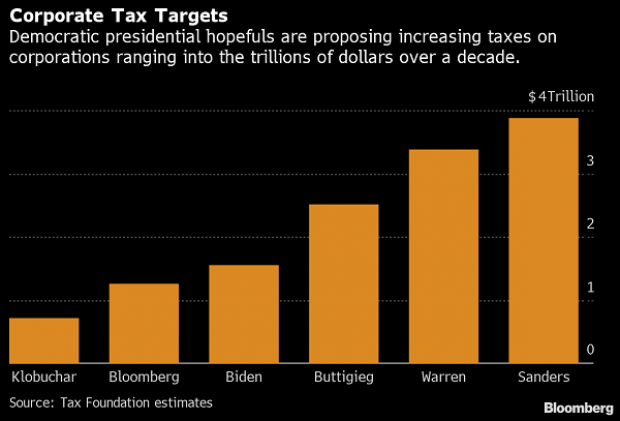
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
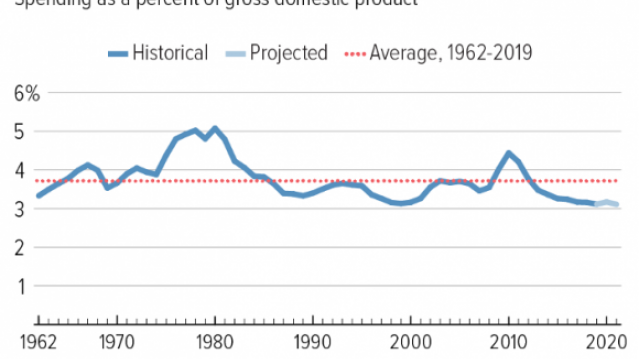
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
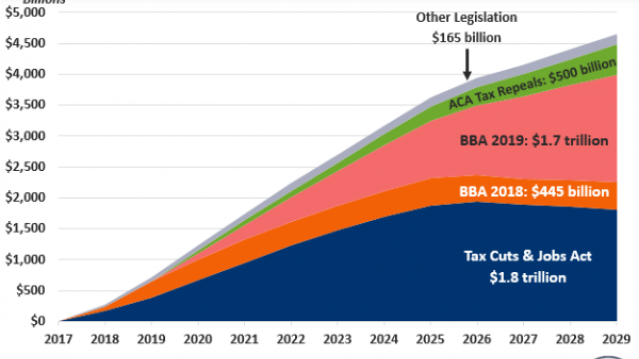
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
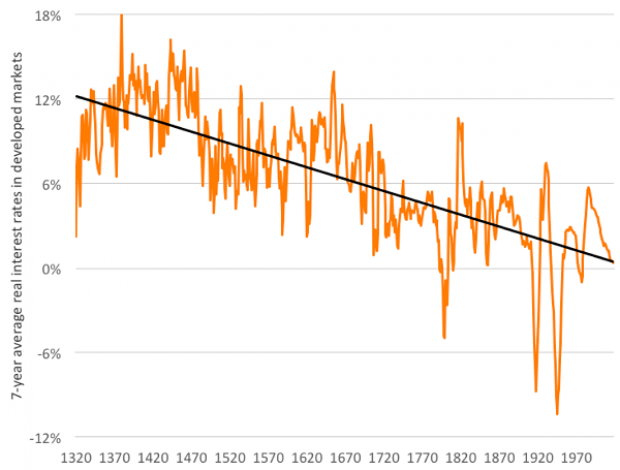
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
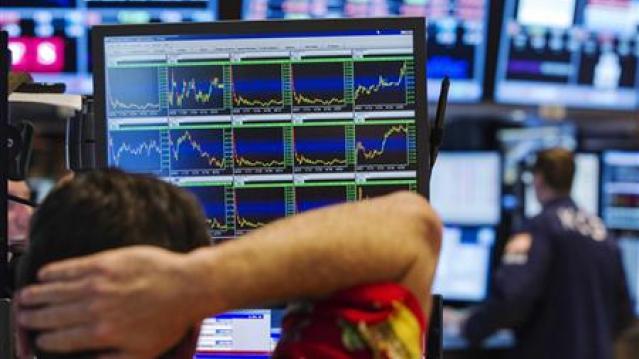
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
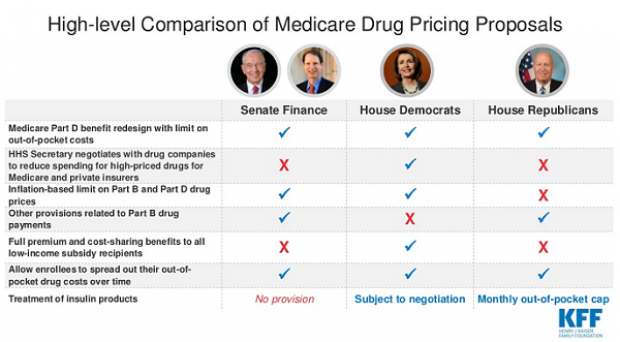
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
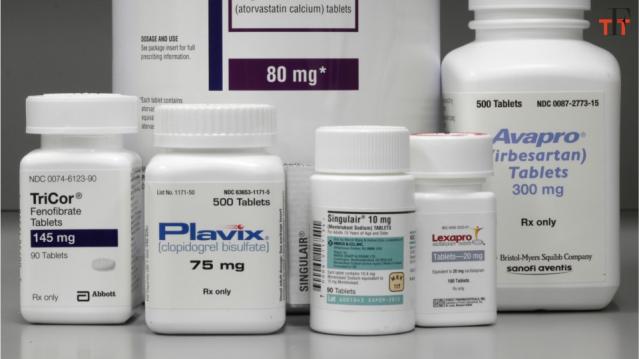
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.