The Crazy Reason Treasury Department Officials Can’t Get Their Work Done
Treasury Department officials are being driven to distraction these days, but it’s not because of the expiring debt ceiling or other pressing financial controversies.
Instead, loud music from a New Orleans-style street band known as Spread Love has reportedly driven some officials and employees at the Treasury building to wear earphones to block out the noise and even move meetings to other parts of the building to find some peace and quiet.
Related: The Next Debt Crisis Could Be Much Worse than in 2013, GAO Warns
“We have to relocate our conference calls,” one Treasury employee told The Washington Post. “We can’t have meetings in that corner of the building anymore. It’s like they’re playing music in the building.”
Members of Spread Love have become fixtures of downtown Washington’s street scene and are collecting generous donations for playing their drums, trombone and other brass instruments. Tourists and other office workers out during their lunch hour appear to love the group, but not so the serious-minded economists and bean counters at the Treasury – especially when the band moves within easy shouting distance at the corner of 15th and G Streets NW.
Treasury Secretary Jack Lew’s staff members aren’t the only ones complaining about the jarring music. Partners and associates at the law firm of Skadden, Arps, Slate, Meagher & Flom find it hard to concentrate on their cases with daily interruptions. It got to the point that the firm dispatched a security guard to offer band members $200 a week if they would play somewhere else. Lonnie Shepard, one of the trombonists, told the newspaper that he laughed at the offer because “We can make that in an hour.”
Related: End of Sanctions Worth Hundreds of Billions to Iran
Rob Runyan, a spokesperson for the Treasury Department, said that employee complaints have made their way to the office of the assistant secretary for management, Brodi Fontenot, but there really wasn’t much that could be done.
“The band and other street noise are part of the distractions of working in downtown D.C.,” Runyan said in an interview Friday.
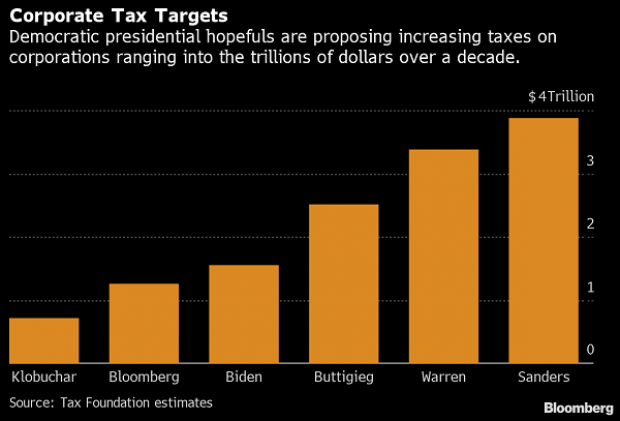
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
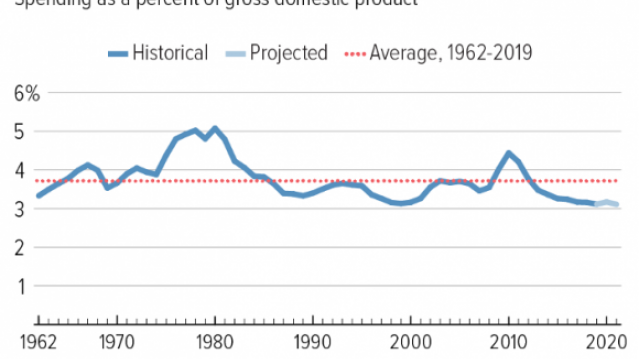
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
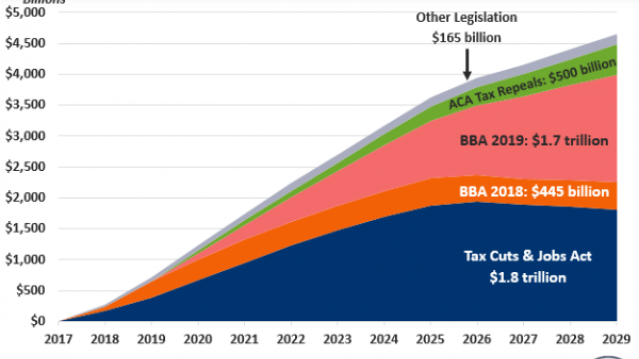
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
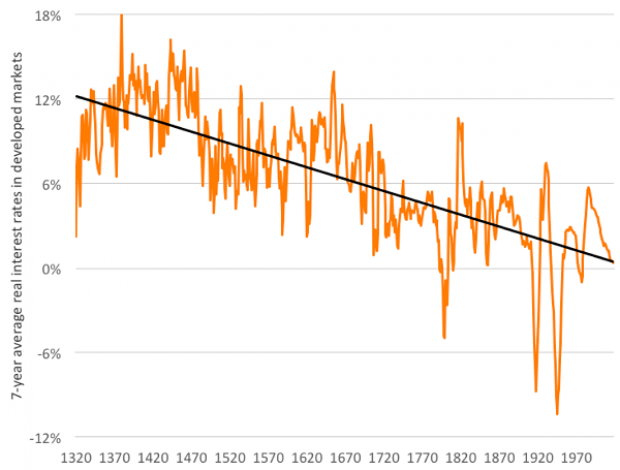
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
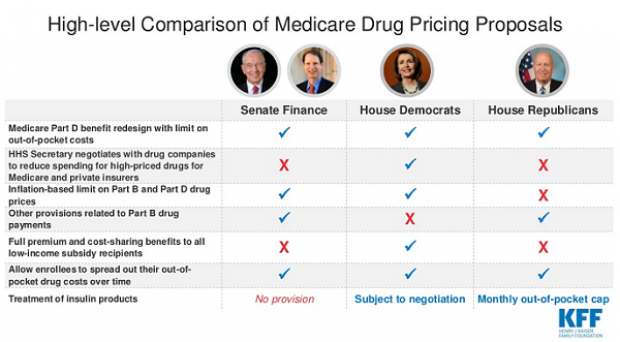
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.