How IBM Is Making Your Passwords Useless
For years, quantum computing has been hailed as a technology that could change the way the modern world works, but a long-standing technical issue has kept that potential from being realized. Now, in a paper published in the journal Nature last week, IBM scientists have taken a big step (see how I avoided the temptation to make a pun there?) toward solving that problem — and while it could represent progress toward making quatum computers real, it also could mean that current cybersecurity standards will soon be much easier to crack. In other words, your passwords could be obsolete soon.
The power of quantum computing has some obvious appeal: The increase in processing power could speed up research, especially in big data applications. Problems with large datasets, or those that need many millions (or billions, or more) of simulations to develop a working theory, would be able to be run at speeds unthinkable today. This could mean giant leaps forward in medical research, where enhanced simulations can be used to test cancer treatments or work on the development of new vaccines for ebola, HIV, malaria and the other diseases. High-level physics labs like CERN could use the extra power to increase our understanding of the way the universe at large works.
But the most immediate impact for the regular person would be in the way your private information is kept safe. Current encryption relies on massively large prime numbers to encode your sensitive information. Using combinations of large prime numbers means that anyone trying to crack such encryption needs to attempt to factor at least one of those numbers to get into encrypted data. When you buy something from, say, Amazon, the connection between your computer and Amazon is encrypted using that basic system (it's more complicated than that, but that's the rough summary). The time it would take a digital computer to calculate these factors is essentially past the heat death of the universe. (Still, this won't help you if your password is password, or monkey, or 123456. Please, people, use a password manager.)
Quantum computing, however, increases processing speed and the actual nature of the computation so significantly that it reduces that time to nearly nothing, making current encryption much less secure.
The IBM researcher that could make that happen is complicated, and it requires some background explanation. For starters, while a "traditional" computing bit can be either a 0 or a 1, a quantum computing bit can have three (or infinite, depending on how you want to interpret the concept) states. More specifically, a qubit can be 0, 1, or both.
 Up until now, the both part of that caused some problems in realizing the power of quantum computing.
Up until now, the both part of that caused some problems in realizing the power of quantum computing.
Apparently — and you'll have to take this on faith a bit, as it hurts my head to think about it — the both state can switch back to either 0 or 1 at any given point, and sometimes incorrectly, based on the logic in the programming. Think about when your phone freezes up for a second or two while you're matching tiles. This is its processor handling vast amounts of information and filtering out the operations that fail for any number of reasons, from buggy code to malware to basic electrical noise. When there are only the two binary states, this is a process that usually happens behind the scenes and quickly.
The hold-up with quantum computing up until now is that the vastly greater potential for errors has stymied attempts to identify and nullify them. One additional wrinkle in this reading quantum states is familiar to anyone with basic science fiction knowledge, or perhaps just the ailurophobics. What if the action of reading the qubit actually causes it to collapse to 0 or 1?
The very smart people at IBM think they've solved this. The actual technical explanation is involved, and well beyond my ability to fully follow, but the gist is that instead of just having the qubits arrayed in a lattice on their own, they are arranged such that neighbors essentially check each other, producing the ability to check the common read problems.
That opens the door to further quantum computing developments, including ones that will make your password a thing of the past. So, does this mean that you need to start hoarding gold? No, not yet. And hopefully before quantum computing reaches commercial, or even simply industrial/governmental levels, a better cyber security method will be in place. Or the robots will have already taken over. I for one welcome them.
Quote of the Day: A Big Hurdle for the Tax Cuts

“He goes in and campaigns on an issue, and the challenge is he then talks about executing drug dealers. Why do you think the press is going to cover the tax cuts if you’ve given them the much more exciting issue?”
-- Grover Norquist, president of tax-cutting advocacy group Americans for Tax Reform, on President Trump’s failure to sell the tax law.
The Obamacare Mandate That Could Produce $12 Billion in Fines in 2018

Republicans effectively eliminated the individual Obamacare mandate in the tax package signed late last year. Although the new regulation reducing the mandate penalty to zero doesn’t take effect until 2019, President Trump has cited the rule change as a victory over the health law so many conservatives oppose. “Essentially, we are getting rid of Obamacare. Some people would say, essentially, we have gotten rid of it," Trump told a crowd in Michigan two weeks ago.
However, many parts of the Affordable Care Act are still in effect and will continue to operate even after the individual mandate is eliminated in 2019.
In particular, the employer mandate, which requires companies with more than 50 employees to offer health benefits or face fine of roughly $2,000 per worker, will continue to play a significant role in the Obamacare system. The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the mandate will produce more than $12 billion in fines in 2018 alone.
Some conservative groups are pushing lawmakers to stop enforcing the employer mandate, but the IRS is still working to enforce the law. According to The New York Times Monday, the IRS is sending out notices to more than 30,000 businesses that have failed to comply.
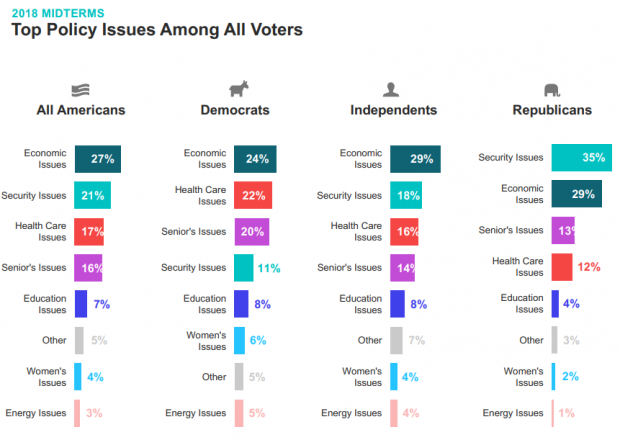
Chart of the Day: It’s Still the Economy, Stupid

Security may be the top policy issue for Republican voters, but the economy is the top concern for Democrats, independents and voters overall, according to Morning Consult’s latest polling on the midterm elections. Health care is third on the list, followed by “seniors’ issues.” The results are based on surveys with more than 275,000 registered U.S. voters from February 1 to April 30.
Number of the Day: $13 Billion

An analysis by Bloomberg finds that the roughly 180 companies in the S&P 500 that have reported earnings for the first three months of the year saved almost $13 billion thanks to the corporate tax cut enacted late last year. Those companies’ effective tax rate dropped by more than 6 percentage points on average. About a third of the tax savings went to 44 financial firms.
How a Florida Doctor with Social Ties to Trump Delayed a $16B Billion VA Project

A West Palm Beach doctor who is friends with Ike Perlmutter, the chairman of Marvel Entertainment and an informal adviser to President Trump on veterans’ issues, has held up “the biggest health information technology project in history — the transformation of the VA’s digital records system,” Politico’s Arthur Allen reports. Dr. Bruce Moskowitz “objected to the $16 billion Department of Veterans Affairs project because he doesn’t like the Cerner Corp. software he uses at two Florida hospitals, according to four former and current senior VA officials. Cerner technology is a cornerstone of the VA project. … Moskowitz’s concerns effectively delayed the agreement for months, the sources said.” Read the full story.