After the Amtrak Crash: Finding the Money to Fix Our Infrastructure

The Amtrak derailment in Philadelphia that left six people dead and dozens more injured has already prompted calls for increased infrastructure spending. "This one is a wake-up call," New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio said Wednesday on MSNBC’s Morning Joe. "We have got to get serious about investing in infrastructure."
There have been other wake-up calls before, and the dire need for infrastructure renewal isn’t news. Yet, as Politico’s Kathryn A. Wolfe reported, the deadly crash occurred just as a House panel was set to mark up a bill that would cut Amtrak’s funding for 2016 to $1.13 billion, or about $250 million less than the railroad service typically gets. (To be fair, it’s also not clear at this point what caused the horrific Amtrak derailment and whether infrastructure problems played a part or not — and the number of rail accidents each year has actually fallen significantly since 2006, according to Federal Railroad Administration data.)
Related: At Least 6 Die in Philadelphia Train Derailment, Scores Hurt
Even before the Amtrak tragedy, though, de Blasio and Oklahoma City Mayor Mick Cornett, a Republican, along with some two dozen other mayors were scheduled to travel to Washington, D.C. today to press Congress for a long-term renewal of the federal transportation authorization bill. The current funding law is set to expire May 31.
Pretty much everyone agrees that it’s well past time for the country to repair and rebuild its dangerously dated bridges, roads, railways, water mains and other critical infrastructure. The hold-up has always been over how to fund it.
Here’s one suggestion: The U.S. has spent some $110 billion on rebuilding Afghanistan, including billions that can’t be accounted for or that the inspector general has found have been wasted. That’s a drop in the bucket compared to the trillions in domestic infrastructure spending that some have called for. Still, clamping down on that waste in Afghanistan, and on other money being frittered away, might allow for some spending to be redirected to other necessary and more productive needs, like domestic infrastructure.
That’s not to suggest we must entirely abandon nation building abroad in order to rebuild this country. It’s just to point out that Congress should be able to find the money to address our national priorities, something it has miserably failed to do of late.
Trump and Schumer Will Try to Scrap the Debt Ceiling
The president and the Senate Democratic leader agreed to seek out a more permanent debt ceiling solution that would end the perpetual cycle of fiscal standoffs. “There are a lot of good reasons to do that, so certainly that’s something that will be discussed," Trump said Thursday. It might not be easy, though, as conservatives see the borrowing limit as a way to keep government spending in check. Paul Ryan said Thursday he opposes doing away with the debt ceiling.
Is a Fix for Obamacare Taking Shape?
Senators on the Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions heard from governors Thursday in the second of four scheduled hearings on stabilizing Obamacare. The common theme emerging from the testimony was flexibility: "Returning control to the states is prudent policy but also prudent politics," said Utah Gov. Gary Herbert, a Republican. He was joined by Democrat John Hickenlooper of Colorado, who said that states need room to innovate and learn from their mistakes. Much of what the governors said was in line with what the Senate panel is already considering, including the continuation of cost-sharing subsidies to insurance companies. (CBS News, Axios)
Senate Approves Trump's Deal with Dems. Will the House Go Along?
The Senate on Thursday voted to fund the government and increase the federal borrowing limit through December 8 as part of a deal that also included $15.25 billion in hurricane disaster relief funding and a short-term extension of the National Flood Insurance Program. The bill passed by a vote of 80-to-17, with only Republicans voting against the bill.
The package now goes back to the House, where it likely faces more strenuous resistance. The Republican Study Committee, a conservative caucus with more than 155 members, on Thursday announced it opposed the deal because it does not include spending cuts. Rep. Mark Walker, the group's chairman, sent a letter to House Speaker Paul Ryan listing 19 policy changes to "address the growing debt burden" or "begin draining the swamp" that could win conservative support for raising the debt ceiling. Some Democrats may also vote against the deal to signal their frustration with an agreement that they say weakened their hand in trying to protect undocumented immigrants who were brought into the country as children.
White House Backs Off Shutdown Threat…for Now
“Believe me, if we have to close down our government, we’re building that wall,” President Trump said of his planned border wall with Mexico 10 days ago. Just two days later, though, White House officials told Congress that a short-term spending bill to fund the government into December wouldn’t have to include $1.6 billion for the wall, The Washington Post reports.
Trump still wants money for the wall to be included in a December budget bill, and he could follow through on his shutdown threat at that point. For now, though, an agreement on a “continuing resolution” to keep the government running after September 30 seems likelier, allowing Congress to deal with some of the other pressing issues it faces this month.
Which Trump Agenda Items Are Companies Talking About With Wall Street?

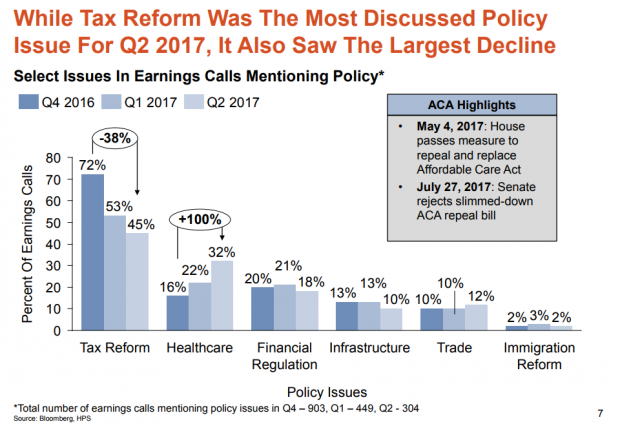
Hamilton Place Strategies, a public affairs consulting firm, analyzed transcripts of earnings calls by publicly traded U.S. companies over the last three quarters. They found that tax reform was the policy issue companies discussed most on those calls with Wall Street analysts — but that mentions of the subject dropped by 38 percent from the fourth quarter of 2016 to the second quarter of 2017. Overall, the percentage of earnings calls mentioning government or policy issues fell from 41 percent to 16 percent. Health-care reform saw the largest increase.
Does this mean that businesses have given up on tax reform this year? Perhaps. More likely, it's simply the result of a lack of action on the tax overhaul. Hamilton Place notes that mentions of tax policy peaked in February just after the Senate Finance Committee advanced Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin's nomination and have spiked after other tax-related announcements. So mentions of tax reform on earnings calls could surge again the fall.
One other note about what businesses have been discussing: Calls mentioning President Trump fell by 84 percent from January to late August.
08312017_HPS_Chart_of_the_day.PNG