Privacy-Focused DuckDuckGo Search Engine Says Traffic Has Soared Since Snowden Leaks

If you haven’t yet heard about DuckDuckGo, you probably will soon.
On its face, the search engine looks much the same as any other. A little more sparse, maybe, but nothing much separating it from, say, Google. There’s a logo and a box for your search.
Where it differs from its peers, though, is what happens when you hit enter.
Though silly in name, DuckDuckGo has a serious ethos: protection of user privacy at all costs. The engine, launched in 2009, shies away from the personalized filter bubbles so adored by search giants like Google and Bing, refusing to track searches or store user data. Users have the option to completely anonymize their search by routing it through the anonymizing TOR network, rendering it even more invisible to prying eyes. DuckDuckGo earns money through simple keyword-targeted advertising, steering clear of the tracking cookies used by more sophisticated ad campaigns.
Though the slavish dedication to privacy has its drawbacks — for example, results are less tailored to the user searching for them, and thus more likely to be irrelevant — the search engine has seen 3 billion searches a year and has a firm community of fans who are attracted to the site’s long-standing defense of user privacy.
Related: News Companies Have Good Reason to Fear Facebook
That ethos seems to be paying off. Gabe Weinberg, CEO of the Pennsylvania-based company, told CNBC last week that the search engine’s traffic has grown 600 percent since Edward Snowden’s 2013 revelations about the large-scale spying conducted by the government. DuckDuckGo’s search traffic was further assisted last year when Apple integrated it into the Safari mobile browser.
DuckDuckGo’s traffic is still tiny compared to the big players — the 3 billion searches a year that Weinberg claimed to have on CNBC is pretty much the same amount of searches that Google traffics in a single day. But DuckDuckGo expects steady growth as average users become increasingly educated about their privacy.
Stat of the Day: 0.2%

The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley tweets: “In order to raise enough revenue to start paying down the debt, Trump would need tariffs to be ~4% of GDP. They're currently 0.2%.”
Read Tankersley’s full breakdown of why tariffs won’t come close to eliminating the deficit or paying down the national debt here.
Number of the Day: 44%

The “short-term” health plans the Trump administration is promoting as low-cost alternatives to Obamacare aren’t bound by the Affordable Care Act’s requirement to spend a substantial majority of their premium revenues on medical care. UnitedHealth is the largest seller of short-term plans, according to Axios, which provided this interesting detail on just how profitable this type of insurance can be: “United’s short-term plans paid out 44% of their premium revenues last year for medical care. ACA plans have to pay out at least 80%.”
Number of the Day: 4,229

The Washington Post’s Fact Checkers on Wednesday updated their database of false and misleading claims made by President Trump: “As of day 558, he’s made 4,229 Trumpian claims — an increase of 978 in just two months.”
The tally, which works out to an average of almost 7.6 false or misleading claims a day, includes 432 problematics statements on trade and 336 claims on taxes. “Eighty-eight times, he has made the false assertion that he passed the biggest tax cut in U.S. history,” the Post says.
Number of the Day: $3 Billion

A new analysis by the Department of Health and Human Services finds that Medicare’s prescription drug program could have saved almost $3 billion in 2016 if pharmacies dispensed generic drugs instead of their brand-name counterparts, Axios reports. “But the savings total is inflated a bit, which HHS admits, because it doesn’t include rebates that brand-name drug makers give to [pharmacy benefit managers] and health plans — and PBMs are known to play games with generic drugs to juice their profits.”
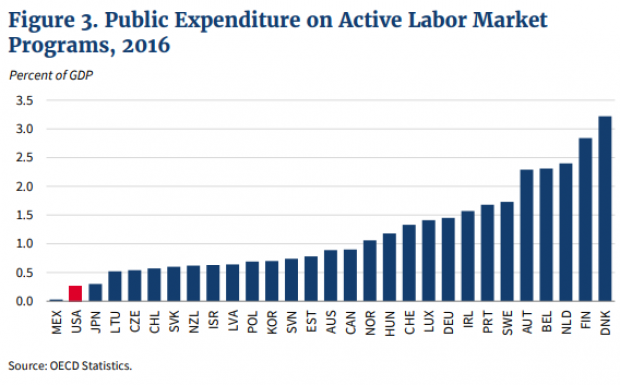
Chart of the Day: Public Spending on Job Programs

President Trump announced on Thursday the creation of a National Council for the American Worker, charged with developing “a national strategy for training and retraining workers for high-demand industries,” his daughter Ivanka wrote in The Wall Street Journal. A report from the president’s National Council on Economic Advisers earlier this week made it clear that the U.S. currently spends less public money on job programs than many other developed countries.