Most Americans Are Happy at Work, but Feeling Burnt Out

They’re working longer days and clocking weekend hours, but nearly nine in 10 employees are still happy at work and motivated to rise in their organizations, according to a new report from Staples Advantage, the business-to-business arm of Staples, Inc.
The study was not all positive, however. Twenty percent of all workers surveyed and 25 percent of millennials said they expected to change jobs in the next year. Many said they feel chained to their desks during the workday, and 53 percent say they are feeling burnt out.
About half of employees polled said that they feel they can’t get up for a break at all, and just under half eat lunch at their desk.
Related: The One Quick Way to Boost Worker Productivity
“While many are still happy at work, we have to ask whether it’s because they’re truly inspired and motivated, or simply conditioned to the new reality?” Dan Schwabel, founder of WorkplaceTrends.com said in a statement. “Either way, employers need to adjust to win the war for talent and optimize productivity, engagement, and loyalty with employees.”
A quarter of employees say they are working after the standard workday has ended, and about 40 percent work at least one weekend per month. More than a third of workers say they put in those extra hours in order to finish work they didn’t have time to get to, and 22 percent say it’s because they want to get ahead for the next day.
The survey also looked at factors that erode employee productivity, with workers citing email overload and inefficient meetings as top factors. One if five workers said that they spend more than two hours per day in meetings.
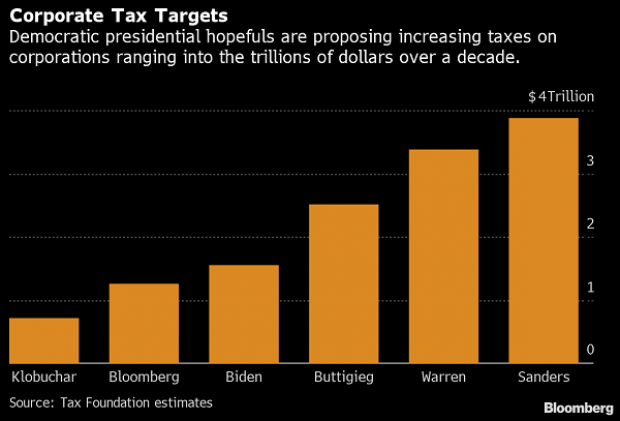
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
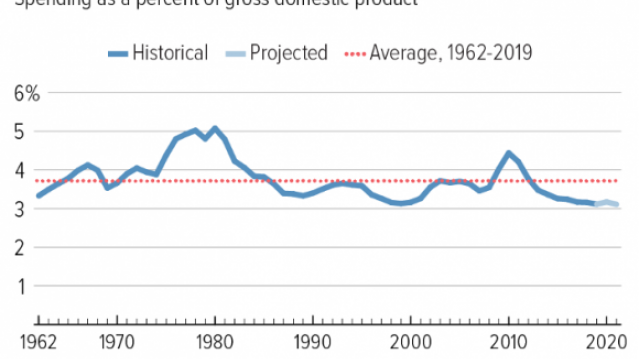
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
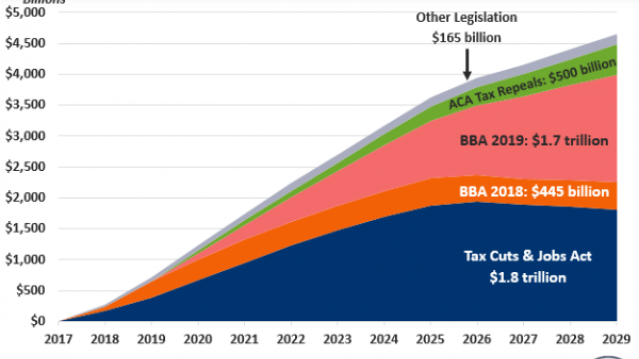
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
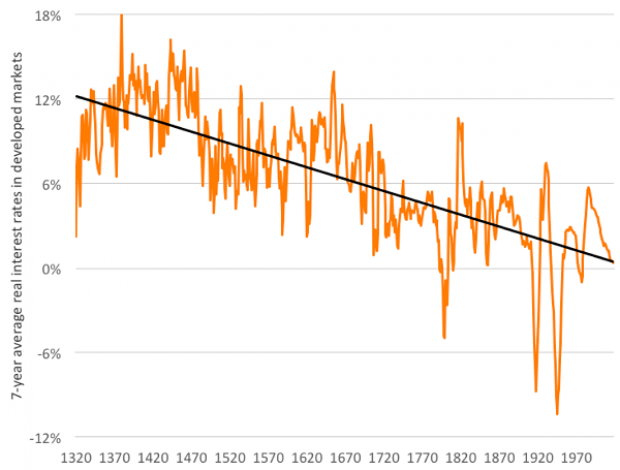
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
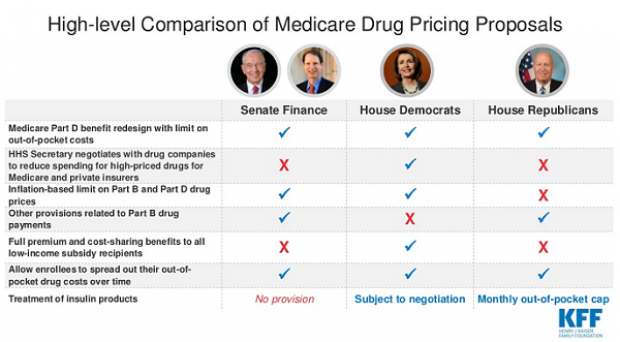
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.