Did Airlines Collude to Keep Air Fares High?

For months now, oil and gas prices have been dropping—and that includes jet fuel. So why haven’t airline ticket prices dropped as well? That’s one of the questions the Justice Department wants answered as it investigates the possibility of collusion among carriers to keep airfares high.
The DOJ also wants to know if companies conspired to limit the number of available seats in order to drive prices up. Yesterday, the Associated Press broke the news that major U.S. carriers had received a letter demanding copies of all communications the airlines had with each other, Wall Street analysts, and major shareholders about their plans for passenger-carrying capacity, going back to January 2010. The civil antitrust investigation is focusing on whether airlines illegally indicated to each other how quickly they would add new flights, routes, and extra seats in an effort to prop up ticket prices.
Related: 6 Sneaky Fees That Are Making Airlines a Bundle
Just minutes after the news broke, stocks of the major U.S. airlines fell four to five percent, with the S&P 500 airlines index off more than four percent. Until now, the U.S. airline industry had been enjoying record profits, due to increasing numbers of Americans flying and a huge drop in the price of jet fuel. In April, the price of jet fuel was $1.94 per gallon, a decrease of 34 percent from the previous year.
The investigation marks a notable shift for the Justice Department, which approved the merger of American Airlines and US Airways back in November 2013, despite previously blocking it over concerns that the airlines would collude on fares. The probe could signal a more aggressive approach on antitrust enforcement, under the strong leadership of Loretta Lynch, who was confirmed in April.
Justice Department spokesperson Emily Pierce confirmed that the department was investigating potential “unlawful coordination” among some airlines.
Just two weeks ago, U.S. Senator Richard Blumenthal (D-CT) urged the Justice Department to investigate what he called “anti-competitive, anti-consumer conduct and misuse of market power in the airline industry.”
Related: United Airlines Bullish on First Quarter from Lower Fuel Costs
Since 2008, various mergers have resulted in four major airlines (down from nine)—American, Delta, Southwest, and United—controlling about 80 percent of all domestic air travel. All four airlines have confirmed that they received the letter and that they were cooperating with the investigation.
According to Bureau of Transportation Statistics, the average domestic airfare rose 13 percent from 2009 to 2014 (adjusted for inflation). The average domestic flight last year cost $391. In the past year alone, airlines received an additional $3.6 billion from bag fees and another $3 billion from reservation-change fees. All of the major airlines—American Airlines, United Continental Holdings, Delta Air Lines, Southwest Airlines, JetBlue Airways, and Alaska Air Group—posted record profits with a consolidated net income of over $3 billion during the first quarter of 2015.
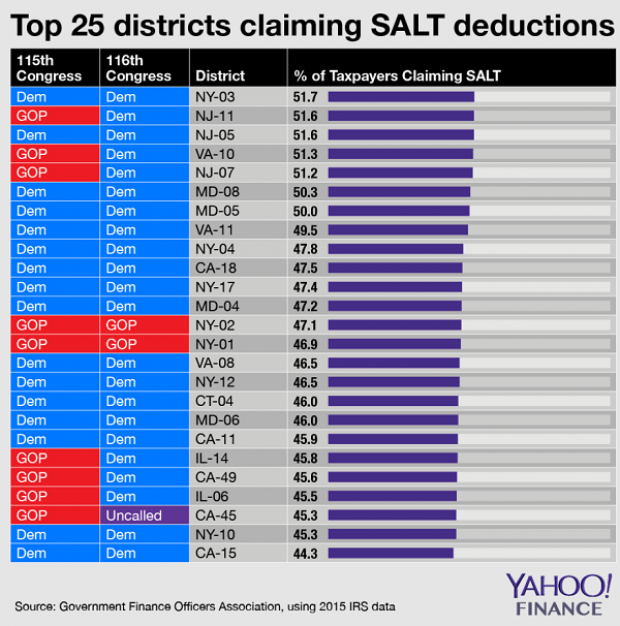
Chart of the Day: SALT in the GOP’s Wounds

The stark and growing divide between urban/suburban and rural districts was one big story in this year’s election results, with Democrats gaining seats in the House as a result of their success in suburban areas. The GOP tax law may have helped drive that trend, Yahoo Finance’s Brian Cheung notes.
The new tax law capped the amount of state and local tax deductions Americans can claim in their federal filings at $10,000. Congressional seats for nine of the top 25 districts where residents claim those SALT deductions were held by Republicans heading into Election Day. Six of the nine flipped to the Democrats in last week’s midterms.
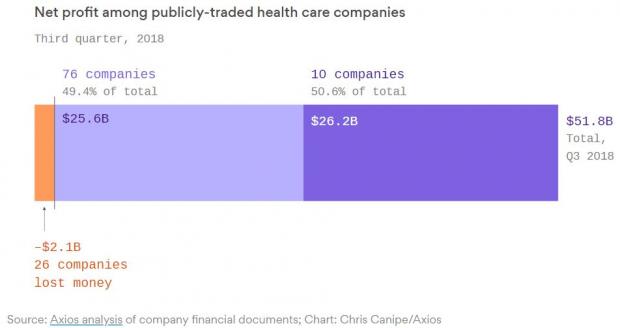
Chart of the Day: Big Pharma's Big Profits
Ten companies, including nine pharmaceutical giants, accounted for half of the health care industry's $50 billion in worldwide profits in the third quarter of 2018, according to an analysis by Axios’s Bob Herman. Drug companies generated 23 percent of the industry’s $636 billion in revenue — and 63 percent of the total profits. “Americans spend a lot more money on hospital and physician care than prescription drugs, but pharmaceutical companies pocket a lot more than other parts of the industry,” Herman writes.
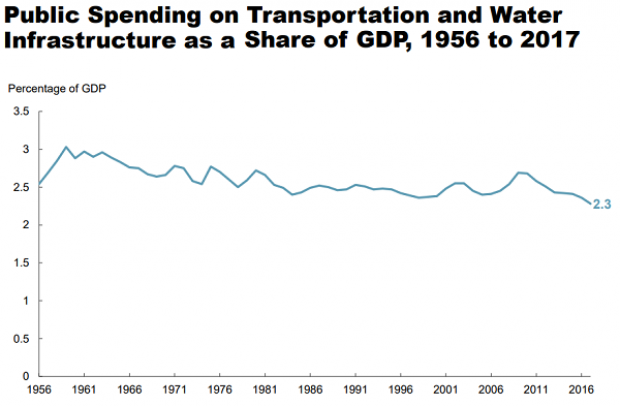
Chart of the Day: Infrastructure Spending Over 60 Years

Federal, state and local governments spent about $441 billion on infrastructure in 2017, with the money going toward highways, mass transit and rail, aviation, water transportation, water resources and water utilities. Measured as a percentage of GDP, total spending is a bit lower than it was 50 years ago. For more details, see this new report from the Congressional Budget Office.
Number of the Day: $3.3 Billion

The GOP tax cuts have provided a significant earnings boost for the big U.S. banks so far this year. Changes in the tax code “saved the nation’s six biggest banks $3.3 billion in the third quarter alone,” according to a Bloomberg report Thursday. The data is drawn from earnings reports from Bank of America, Citigroup, Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, Morgan Stanley and Wells Fargo.
Clarifying the Drop in Obamacare Premiums

We told you Thursday about the Trump administration’s announcement that average premiums for benchmark Obamacare plans will fall 1.5 percent next year, but analyst Charles Gaba says the story is a bit more complicated. According to Gaba’s calculations, average premiums for all individual health plans will rise next year by 3.1 percent.
The difference between the two figures is produced by two very different datasets. The Trump administration included only the second-lowest-cost Silver plans in 39 states in its analysis, while Gaba examined all individual plans sold in all 50 states.