They’re Leaving Las Vegas: Fewer I Do’s in Last Decade

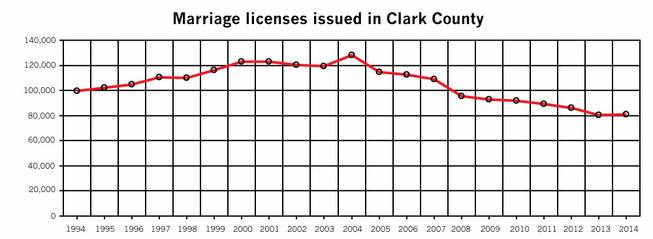
When it comes to destination weddings, Las Vegas has lost that loving feeling. The Las Vegas Sun reports that the wedding rate in Sin City has plummeted 37 percent in the past decade—nearly 47,000 fewer couples got married in 2014 than in 2004.
By comparison, 2004 was a boom year for weddings in Sin City. There were 128,000 weddings that year—including Britney Spears’ 55-hour marriage to Jason Allen Alexander at A Little White Wedding Chapel.
Related: Marriage?? Young Americans Aren’t Even Shacking Up
Who knows why gambling on love in Sin City has become a losing bet? Perhaps the dip reflects a national trend of millennials waiting to tie the knot or choosing to stay single. The marriage rate in the U.S. neared a record low in 2015 and is expected to drop further in 2016. Then there’s the expense. According to the TheKnot, the average wedding cost (excluding the honeymoon) is $31,213, with many couples looking for more unusual venues.
Clark County Clerk Lynn Goya, who took office in January, wants to change that trend in Vegas. The current fee for a marriage license in Las Vegas is $60, but Goya is asking for a $14 increase in the cost of wedding licenses to support marketing efforts targeting engaged couples. Last year 81,000 weddings happened in Las Vegas—and she’s hoping that wedding vow renewals and gay weddings will help boost those numbers even more. In New York, the legalization of gay marriage in 2011 led to an estimated $259 million in spending and $16 million in revenues for New York City.
Related: The $2.6 Billion Gay Wedding Boom
Then again it may be hard for Las Vegas to shake that quickie, drive-thru wedding image. Sin City has always had an illustrious history of celebrity weddings, with many more misses than hits: Cher’s nine-day union to rocker Gregg Allman in 1975, Mia Farrow and Frank Sinatra in 1966, Demi Moore and Bruce Willis in 1987, Richard Gere and Cindy Crawford in 1991, and Angelina Jolie and Billy Bob Thornton in 2000. On the bright side, there’s Paul Newman and Joanne Woodward’s marriage, which endured for 50 years, Jon Bon Jovi and his wife, Dorothea’s 1987 wedding day, and Kelly Ripa and Mark Consuelo’s union from 1996, which is still standing.
Trump: Repeal the Obamacare Mandate to Cut the Top Tax Rate

President Trump repeated his call Monday to repeal the Affordable Care Act’s individual mandate as part of the tax bill. In a tweet — geotagged from Pennsylvania, not the Philippines , where Trump currently is — Trump added that the billions in savings from ending the mandate should be used to cut the top marginal rate to 35 percent and the rest on cuts for the middle class.
The Congressional Budget Office said last week that eliminating the mandate would save $338 billion over the next decade.
The current version of the House tax bill keeps the top individual income tax rate at 39.6 percent, while the Senate bill lowers it to 38.5 percent. However, mandate repeal is not currently part of either tax bill, and, as The New York Times notes, “repeal of the individual mandate was not on the list of 355 amendments that the [Senate Finance Committee] released on Sunday night.”
Tax Reform Is Hard, but the GOP Could Have Made This Easier
The Tax Policy Center’s William G. Gale writes that the GOP’s approach to the tax bill combines a $5.8 trillion tax cut with a $4.3 trillion tax increase to offset the costs. There may have been an easier way. “What if the House GOP simply tried to cut business and individual taxes by $1.5 trillion. No offsets needed. They could have distributed small tax cuts to middle-income individuals by, say, modestly expanding the earned income tax credit and raising the standard deduction. And they could have trimmed the top corporate tax rate by a few percentage points. It would not have been base-broadening tax reform, but neither is the current bill. ... Tax reform is never easy, but crafting the bill this way has vastly increased the challenge of passing it.”
Alan Greenspan: Deal with the National Debt Before Cutting Taxes

Former Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan is warning that sharply cutting taxes right now would be an economic “mistake.”
In an interview with Maria Bartiromo on the Fox Business Network Thursday, the 91-year-old Greenspan said it’s more important for President Trump and Congress to put the nation on a sustainable fiscal path by addressing rising entitlement spending driven by the aging of the U.S. population.
“Frankly, I think what we ought to be concerned about is the fact the federal debt is rising at a very rapid pace, and there’s nothing in this bill that will essentially stop that from happening," Greenspan said. "So my view is that we’re premature on fiscal stimulus, whether it’s tax cuts or expenditure increases. We’ve got to get the debt stabilized before we can even think in those terms.”
GOP’s Estate-Tax Repeal Details Would Save Super-Rich Tens of Billions Extra

It’s no surprise that the House Republicans’ tax bill includes the eventual repeal of the estate tax, a long-held GOP goal. But The Washington Post’s Glenn Kessler highlights an unexpectedly generous aspect of the current bill: It “allows the beneficiaries of estates to not pay capital gains taxes on the increase in value of assets held by the estates. That has not been a feature of most previous estate-tax bills.”
Currently, estates face a federal tax if they’re valued at more than $5.49 million for individuals or almost $11 million for couples. But, for tax purposes, the value of assets passed on to heirs gets “stepped-up” or reset to their value at the time of death. Kessler’s example: “Imagine a home that had been purchased for $250,000 but was now worth $1 million. The ‘stepped-up basis’ would be $1 million. If the heirs sold the house for $1.1 million, they would only owe capital-gains tax on the $100,000 difference, not the $850,000 difference from the original purchase price.”
The GOP bill repeals the estate tax, but also keeps the stepped-up basis — a seemingly small detail that creates a huge tax shelter. It means that heirs of large estates would save tens of billions of dollars a year when they sell assets that have appreciated in value over time — or, as Kessler puts it, that the bill will allow “tens of billions of untapped capital gains to remain beyond the reach of the U.S. government.”
Republicans Are Still Coming After Obamacare’s Individual Mandate

Speaker Paul Ryan said Sunday that House Republicans are still considering a repeal of the Obamacare individual mandate as part of their tax bill. "We have an active conversation with our members and a whole host of ideas on things to add to this bill. And that’s one of the things that’s being discussed," Ryan said on Fox News. President Trump touted the idea in a tweet last week, and Sens. Tom Cotton and Rand Paul have recently spoken in favor of using the tax bill to eliminate the mandate. The move would save the government $416 billion over 10 years as roughly 15 million people go without insurance due to lower spending on subsidies and health care services, according to the CBO. Those savings could be appealing as Republicans look for revenues in their revised tax bill. But if the controversial repeal of the mandate isn’t included in the tax bill, the White House is reportedly ready to roll out an executive order weakening the requirement that taxpayers provide proof of insurance to avoid paying a penalty.