This Is the Most Annoying Thing About Customer Service

The number of Americans fed up with lousy customer service is decreasing but there are still some practices that irritate nearly everyone, according to a newly published report in Consumer Reports’ September issue.
There was a tie for the top customer service complaint. Seventy-five per percent of shoppers surveyed were annoyed by the inability to get a live person on the phone and by dealing with a representative who was rude or condescending.
Seventy-four percent of consumers said they were highly annoyed at being disconnected from a customer service rep, and 71 percent were dissatisfied that they’d been disconnected and then unable to reach the same representative again.
“Many companies today are simply awful at resolving customer protections, despite investments in whiz-bang technologies and considerable advertising about their customer focus,” Scott Broetzman, president of Customer Care Measurement & Consulting, told the magazine.
In a separate report released this week, 24/7 Wall Street found that Amazon.com is the best big company for customer service, followed by Chick-fil-A and Apple. The companies in the publication’s “Customer Service Hall of Shame” include Bank of America, DirectTV and Comcast.
In order to get the best possible customer service, Consumer Reports recommends using the phone, rather than email; showing—and asking for—empathy; and escalating when necessary.
The magazine also suggests putting technology to work. The website Dial a Human can help find the best customer service number for a company, and the service Lucy Phone lets you enter a company’s name and number and then calls you when a rep becomes available so you don’t have to wait on hold.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- The Next Debt Crisis Could Be Much Worse than in 2013, GAO Warns
- The New Generation of ‘Genuinely Creepy’ Electronic Devices
- Who Are These People Giving Money to Donald Trump?
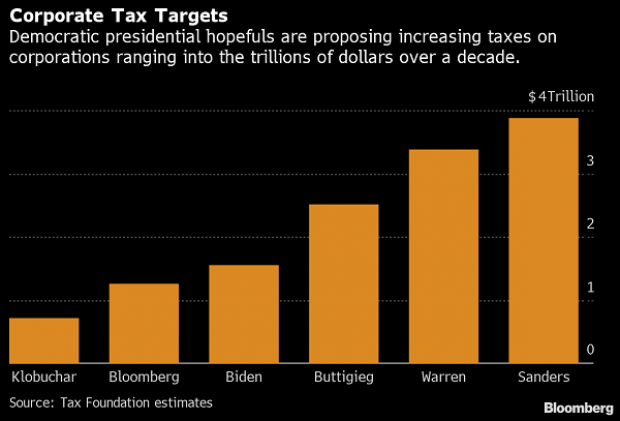
Chart of the Day: Boosting Corporate Tax Revenues

The leading candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination have all proposed increasing taxes on corporations, including raising income tax rates to levels ranging from 25% to 35%, up from the current 21% imposed by the Republican tax cuts in 2017. With Bernie Sanders leading the way at $3.9 trillion, here’s how much revenue the higher proposed corporate taxes, along with additional proposed surtaxes and reduced tax breaks, would generate over a decade, according to calculations by the right-leaning Tax Foundation, highlighted Wednesday by Bloomberg News.
Chart of the Day: Discretionary Spending Droops
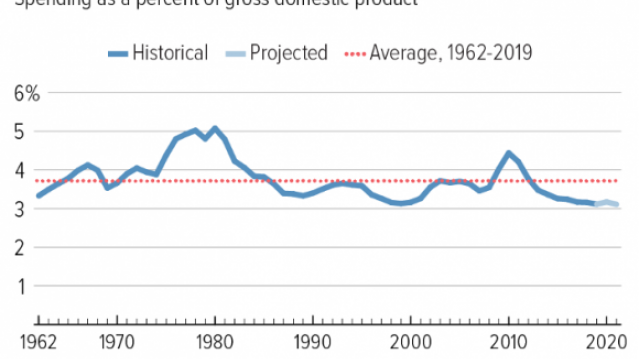
The federal government’s total non-defense discretionary spending – which covers everything from education and national parks to veterans’ medical care and low-income housing assistance – equals 3.2% of GDP in 2020, near historic lows going back to 1962, according to an analysis this week from the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Chart of the Week: Trump Adds $4.7 Trillion in Debt
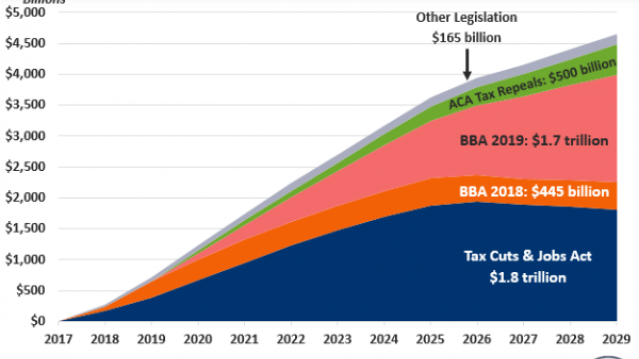
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget estimated this week that President Trump has now signed legislation that will add a total of $4.7 trillion to the national debt between 2017 and 2029. Tax cuts and spending increases account for similar portions of the projected increase, though if the individual tax cuts in the 2017 Republican overhaul are extended beyond their current expiration date at the end of 2025, they would add another $1 trillion in debt through 2029.
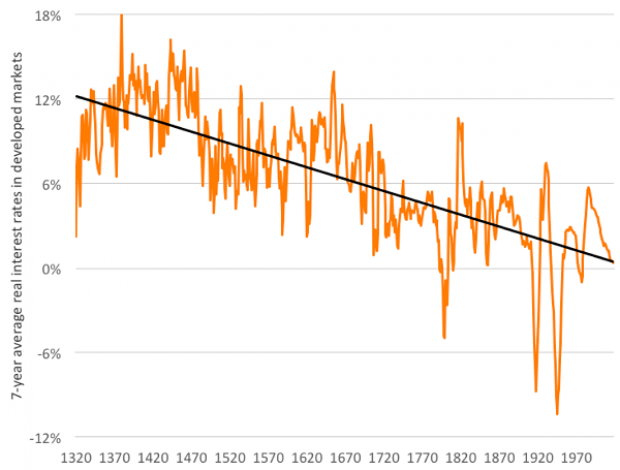
Chart of the Day: The Long Decline in Interest Rates
Are interest rates destined to move higher, increasing the cost of private and public debt? While many experts believe that higher rates are all but inevitable, historian Paul Schmelzing argues that today’s low-interest environment is consistent with a long-term trend stretching back 600 years.
The chart “shows a clear historical downtrend, with rates falling about 1% every 60 years to near zero today,” says Bloomberg’s Aaron Brown. “Rates do tend to revert to a mean, but that mean seems to be declining.”
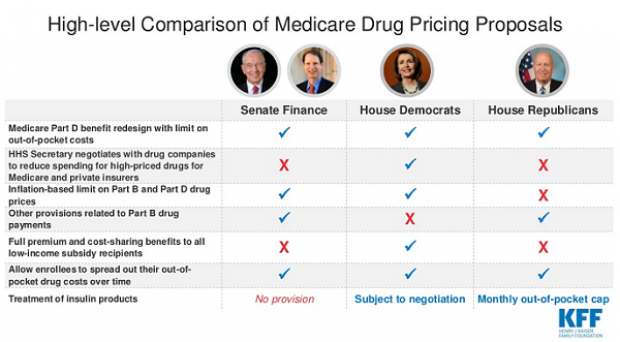
Chart of the Day: Drug Price Plans Compared
Lawmakers are considering three separate bills that are intended to reduce the cost of prescription drugs. Here’s an overview of the proposals, from a series of charts produced by the Kaiser Family Foundation this week. An interesting detail highlighted in another chart: 88% of voters – including 92% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans – want to give the government the power to negotiate prices with drug companies.