Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
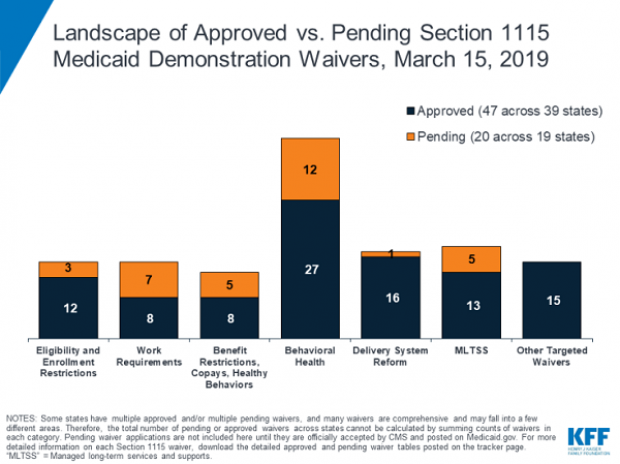
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
Fitch Sends a Warning on US Credit Rating
One of the three major credit ratings agencies warned Wednesday that a failure to raise the debt ceiling could result in a lower credit rating for the U.S.
Fitch Ratings currently assigns a AAA rating to U.S. debt, the highest level possible. However, a failure to raise the debt ceiling "may not be compatible with 'AAA' status," according to the agency.
If the U.S. cannot sell more debt after bumping up against the debt ceiling, it may not be able to make all of its interest payments on time and in full. The federal government could begin running out of cash as soon as October.
The debt ceiling is currently $19.9 trillion, and Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin has repeatedly urged Congress to raise the debt ceiling by September 29. A failure to do so could roil financial markets around the world, and ultimately increase the cost of servicing U.S. debt.
This is not the first time Congress has faced this problem. During an earlier debt ceiling showdown in 2011, Standard & Poor's reduced its rating on U.S. debt from its highest level to AA+. However, Fitch and Moody’s stuck with their top ratings.
Senators to Hold Hearings on a Bipartisan Fix for Health Care
Mark your calendars: Senate health committee Chairman Lamar Alexander (R-Tenn.) and Ranking Member Patty Murray (D-Wash.) announced today that they will hold bipartisan hearings on Sept. 6 and 7 focused on stabilizing premiums in the individual insurance market. The first hearing will be with state insurance commissioners; the second will be with governors.
In a statement, Alexander noted that 18 million Americans buy insurance on the individual market.
“My goal by the end of September is to give them peace of mind that they will be able to buy insurance at a reasonable price for the year 2018,” he said. “Unless Congress acts by September 27—when insurance companies must sign contracts with the federal government to sell insurance on the federal exchange in 2018— 9 million Americans in the individual market who receive no government help purchasing health insurance and whose premiums have already skyrocketed may see their premiums go up even more. Even those with subsidies in up to half our states may find themselves with zero options for buying health insurance on the Obamacare exchanges in 2018.”
McConnell: ‘Zero Chance’ the Debt Ceiling Will Be Breached
At an event in Kentucky to discuss tax reform, Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell and Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin insisted Monday that Congress will raise the debt ceiling by late next month, in time for the U.S. to avoid a default that could roil the global economy and markets.
Related: The Debt Ceiling — What It Is and Why We Should Care
The key quotes, per Roll Call:
McConnell: "There is zero chance — no chance — we won't raise the debt ceiling. No chance. America's not going to default. And we'll get the job done in conjunction with the secretary of the Treasury."
Mnuchin: “We’re going to get the debt ceiling passed. I think that everybody understands this is not a Republican issue, this is not a Democrat issue. We need to be able to pay our debts. This is about having a clean debt ceiling so that we can maintain the best credit, the reserve currency, and be focused on what we should be focusing on — so many other really important issues for the economy.”
Related: Here’s a Solution for the Annual Debt Ceiling Crisis — Get Rid of It
Mnuchin reiterated his “strong preference” for a “clean” increase to the debt limit — one without other policy proposals or spending cuts attached to it — but some House conservatives continue to press for such cuts.
Bonus McConnell quote on what tax breaks might be eliminated in tax reform: “I think there are only two things that the American people think are actually in the Constitution: The charitable deduction and the home mortgage interest deduction. So, if you’re worried about those two, you can breathe easy. For all the rest of you, there’s no point in doing tax reform unless we look at all of these preferences, and carried interest would be among them.”
Trump’s Travel and Family Size Squeeze Secret Service Budget
In an interview with USA Today, Secret Service Director Randolph "Tex" Alles said the agency is bumping up against federally mandated salary and overtime caps in executing its mission to protect the president and his family.
USA Today’s Kevin Johnson notes that 42 people in the Trump administration have Secret Service protection, including 18 of the president’s family members. Under President Obama, 31 people had such protection.
“The compensation crunch is so serious that the director has begun discussions with key lawmakers to raise the combined salary and overtime cap for agents, from $160,000 per year to $187,000 for at least the duration of Trump's first term,” Johnson reported.
Related: Which Former President Costs US the Most?
In a statement, Alles said the agency has the funding it needs for the rest of the fiscal year, which runs through Sept. 30, but estimated that 1,100 employees run into statutory pay caps as a result of overtime work during this calendar year.
“This issue is not one that can be attributed to the current Administration’s protection requirements alone, but rather has been an ongoing issue for nearly a decade due to an overall increase in operational tempo," Alles said in the statement.
Earlier: The Secret Service Won’t Get $60 Million More to Protect the Trumps
Will Trump's Tax Cuts Really Happen? Economists Are Surprisingly Optimistic
Despite all the thorny questions swirling around President Trump's nascent tax reform plan, 29 of 38 economists surveyed by Bloomberg in a monthly poll said they expect Congress to cut taxes by November of next year.
The hitch: The economists don’t expect the cuts will help the economy much. The median projection of a larger group of 71 economists is for 2018 growth of 2.3 percent, up only slightly from 2.1 percent this year — and by 2019, the economists see growth slipping back to 2 percent.