Privacy-Focused DuckDuckGo Search Engine Says Traffic Has Soared Since Snowden Leaks

If you haven’t yet heard about DuckDuckGo, you probably will soon.
On its face, the search engine looks much the same as any other. A little more sparse, maybe, but nothing much separating it from, say, Google. There’s a logo and a box for your search.
Where it differs from its peers, though, is what happens when you hit enter.
Though silly in name, DuckDuckGo has a serious ethos: protection of user privacy at all costs. The engine, launched in 2009, shies away from the personalized filter bubbles so adored by search giants like Google and Bing, refusing to track searches or store user data. Users have the option to completely anonymize their search by routing it through the anonymizing TOR network, rendering it even more invisible to prying eyes. DuckDuckGo earns money through simple keyword-targeted advertising, steering clear of the tracking cookies used by more sophisticated ad campaigns.
Though the slavish dedication to privacy has its drawbacks — for example, results are less tailored to the user searching for them, and thus more likely to be irrelevant — the search engine has seen 3 billion searches a year and has a firm community of fans who are attracted to the site’s long-standing defense of user privacy.
Related: News Companies Have Good Reason to Fear Facebook
That ethos seems to be paying off. Gabe Weinberg, CEO of the Pennsylvania-based company, told CNBC last week that the search engine’s traffic has grown 600 percent since Edward Snowden’s 2013 revelations about the large-scale spying conducted by the government. DuckDuckGo’s search traffic was further assisted last year when Apple integrated it into the Safari mobile browser.
DuckDuckGo’s traffic is still tiny compared to the big players — the 3 billion searches a year that Weinberg claimed to have on CNBC is pretty much the same amount of searches that Google traffics in a single day. But DuckDuckGo expects steady growth as average users become increasingly educated about their privacy.
You’ve Got to See This GOP Hawk’s Grisly Ad Opposing the Iran Deal

A group led by John Bolton, the aggressively hawkish Republican insider who served as George W. Bush's ambassador to the United Nations, has released an unusually grisly ad that vividly portrays a nuclear attack on the United States.
The 30-second video was produced by the Foundation for American Security and Freedom, which Bolton leads. It shows an all-American family of four sitting down to a dinner of pasta and red sauce. The father kindly asks, “How was your day?” As his wife and children enthusiastically reply, a blinding flash rips through the scene to the sound of burning and destruction. The screen fades to black, and then we see and hear Sen. Rand Paul speaking, with his words also written on the screen: “Rand Paul: ‘our national security is not threatened by Iran having one nuclear weapon’.” The screen fades to black again, and then we see a nuclear explosion, with the words: “It only takes one.” As the nuclear cloud boils up into the sky, we see the final message: “A nuclear threat is a threat to our national security.”
The 30-second video seems to consciously mimic Lyndon Johnson's infamous "Daisy" ad from the 1964 presidential election. That ad was widely criticized for using a nuclear explosion to frighten the audience into believing that, if elected, Republican nominee Barry Goldwater would risk all-out war with the Soviet Union. The ad was shown only once (on September 7, 1964) but that proved to be enough.
Several differences between the Bolton group’s ad and “Daisy” stand out. For one, the new ad shows a family being destroyed by a nuclear blast. By contrast, the Johnson ad implied the death of a small girl and many others, but without showing the blast and its victims together.
Another difference is the target. The “Daisy” ad took aim at a hawkish Republican candidate for president, implying that an aggressive attitude toward a major enemy could lead to the destruction of the world. The Bolton group’s ad takes aim at a dovish Republican candidate — and, by implication, a dovish American president — while suggesting that a diplomatic approach toward a major enemy could lead to war on American soil.
A final difference: The Johnson campaign withdrew the “Daisy” ad as the criticism poured in. The Bolton group’s ad is on the Internet, where it can be seen over and over again. And thanks to the dynamics of social media, it will likely reach a larger audience than “Daisy” ever did — though to what effect, it remains to be seen.
Here’s the Daisy ad:
Fast Cars and Rampaging Dinosaurs Help Universal Shatter Box Office Record

High-speed car chases, dinosaurs run amok and yellow, pill-like creatures helped Universal Pictures bring in more money this year than any other studio in movie history.
Universal announced Wednesday that the studio has grossed $5.53 billion in worldwide box office so far this year, setting an industry record. The Comcast-owned studio has pulled in $3.59 billion internationally and $1.94 billion domestically.
Related: ‘Jurassic World’ set to become fastest film to gross $1 billion
Three global box office hits -- “Furious 7,” “Jurassic World” and “Minions” -- were the most successful films for the studio. “Furious 7” and “Jurassic World” have each brought in over $1 billion already, with “Minions” expected to top $1 billion after its Sept. 13 debut in China. Universal is expected to become the first studio to release three films in one year that each took in over $1 billion.
And there are still some big films slated to be released by Universal before the year is out, including the N.W.A. biopic “Straight Outta Compton,” “Steve Jobs,” and the Tina Fey and Amy Poehler comedy “Sisters.”
20th Century Fox held the previous record for annual box office, grossing $5.52 billion in 2014.
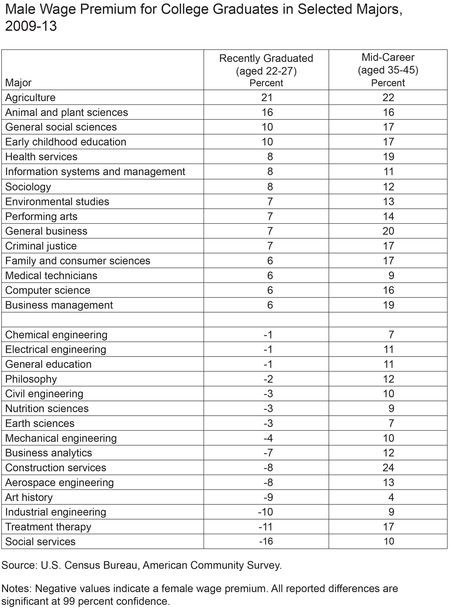
These Women Are Now Earning Almost as Much as Men

That women earn 77 cents for every dollar a man makes has been chronicled and discussed at length, but a new analysis by economists at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York finds a far smaller gap among recent grads.
The country’s youngest (ages 22 to 27) female workers earn roughly 97 cents on the dollar compared to their male peers, when controlling for major and field of employment. For many majors, they actually earn more.
Any early advantage disappears, however, once workers hit mid-career, with men earning 15 percent more than women across the board. Even in majors where women earned more during the early years of their careers, men earn more by age 35.
Related: 10 Worst States for Working Mothers
Researchers point to several potential reasons for the reversal, including possible gender discrimination and women’s tendency to scale back their careers to bear and raise children.
“Because raising a family often requires more flexible schedules, those with family responsibilities who have difficulty satisfying time-sensitive work demands may face lower wages in these types of jobs,” the authors write. “In fact, in jobs where such time demands are largely absent, and more flexibility is possible, the pay gap has been found to be much smaller.”
For some women, that means leaving the workforce entirely. The percentage of women age 25 to 54 who are working has fallen to 69 percent since peaking in 1999 at 74 percent, following a 60-year climb.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
Facebook Patents a Technology That Could Use Your Social Network Against You

All that data Facebook has been gathering on you and your friends could someday be used to approve -- or deny -- your application for a loan.
Facebook was just granted an updated technology patent for “authorization and authentication based on an individual's social network.” This innocent-sounding technology can no doubt be applied in a multitude of ways, many of them benign. But one troubling use of the technology consists of assisting lenders in discriminating against a borrower based on his or her social network connections.
The patent application explains that a lender can use the technology to examine the credit ratings of members of the social network of the individual who is applying for a loan. If the average credit rating of the social network reaches a minimum, pre-defined level, the lender moves forward with the loan process. If the average credit score is too low, the loan application is rejected.
Related: Now Facebook Wants to Know Where You Buy Your Toothpaste
The new technology raises concerns about potential unjust bias, but banks would most likely use it as an additional factor in the loan approval process, not as an end-all metric. The Equal Credit Opportunity Act imposes strict guidelines as to what factors creditors can use when determining whether to approve a loan. It’s unclear if Facebook’s new technology falls under the criteria the federal law defines – things like income, expenses, debt and credit history.
Another fear involves predatory lenders. People rejected for loans through this process would make a nice customer list for unscrupulous financial operators.
Some of the less worrisome uses of the technology include preventing spam email and inappropriate content and improving the accuracy of searches. At this point, it’s not clear how Facebook plans to implement the new technology. Let’s hope the social networking giant stays on the sunny side of the street on this one.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- The 10 Fastest-Growing Jobs Right Now
- Teens Are Having Much Less Sex Than Their Parents Did at That Age
- 9 Social Security Tips You Need to Know Right Now
Facebook Patents a Technology That Could Use Your Social Network Against You

All that data Facebook has been gathering on you and your friends could someday be used to approve -- or deny -- your application for a loan.
Facebook was just granted an updated technology patent for “authorization and authentication based on an individual's social network.” This innocent-sounding technology can no doubt be applied in a multitude of ways, many of them benign. But one troubling use of the technology consists of assisting lenders in discriminating against a borrower based on his or her social network connections.
The patent application explains that a lender can use the technology to examine the credit ratings of members of the social network of the individual who is applying for a loan. If the average credit rating of the social network reaches a minimum, pre-defined level, the lender moves forward with the loan process. If the average credit score is too low, the loan application is rejected.
Related: Now Facebook Wants to Know Where You Buy Your Toothpaste
The new technology raises concerns about potential unjust bias, but banks would most likely use it as an additional factor in the loan approval process, not as an end-all metric. The Equal Credit Opportunity Act imposes strict guidelines as to what factors creditors can use when determining whether to approve a loan. It’s unclear if Facebook’s new technology falls under the criteria the federal law defines – things like income, expenses, debt and credit history.
Another fear involves predatory lenders. People rejected for loans through this process would make a nice customer list for unscrupulous financial operators.
Some of the less worrisome uses of the technology include preventing spam email and inappropriate content and improving the accuracy of searches. At this point, it’s not clear how Facebook plans to implement the new technology. Let’s hope the social networking giant stays on the sunny side of the street on this one.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- The 10 Fastest-Growing Jobs Right Now
- Teens Are Having Much Less Sex Than Their Parents Did at That Age
- 9 Social Security Tips You Need to Know Right Now
