The Fiscal Times Newsletter - August 28, 2017
|
The Woefully Distorted Federal Policies on Child Abuse
Here’s something just in from the world of grossly distorted government policy:
Every year, roughly 680,000 children are reported victims of neglect or abuse by their parents in this country – a tragic statistic reflective of troubling societal, psychological and economic problems. Even worse, 1,520 children died from maltreatment in 2013, nearly 80 percent of them at the hands of their own parents.
Related: Feds Blow $100 Billion Annually on Incorrect Payments
Federal and state authorities over the years have developed a large and costly system for reporting and investigating maltreatment, removing endangered children from their homes, and preventing and treating problems of parents and children.
But as a new study touted on Wednesday by the Brookings Institution concludes, the federal government provides states with far more money to support kids once they have been removed from their homes and placed in foster care than it provides for prevention and treatment programs to keep the kids out of foster homes in the first place.
And the disparity is startling.
Two of the largest grant programs in Title IV-B of the Social Security Act provide states with funding totaling around $650 million annually for “front end” services designed to prevent or treat parent and child problems that contribute to abuse and neglect. They address problems such as substance abuse, family violence and mental health issues.
Related: Time to Stop Social Safety Net Child Abuse
Yet another series of programs in Title IV-E of the Social Security law provides states with open-ended funding that totaled about $6.9 billion in 2014. Those funds pay almost exclusively for out-of-home care for children from poor families, along with the administrative and training expenses associated with foster care, adoption, and guardianship.
That’s a 10 to 1 disparity in funding for the two efforts – one to try to hold families together and the other to move children out of their homes and into foster care.
“Congress has the opportunity to change the funding formula under Title IV of the Social Security Act so that states have the flexibility to put money where it will be most effective at keeping at-risk children safe, ensuring that they have a permanent home, and promoting their well-being,” wrote Ron Haskins, Lawrence M. Berger and Janet Currie, the authors of the study.
In their policy brief, “Can States Improve Children’s Health by Preventing Abuse and Neglect,” Haskins, a Senior Fellow in Economic Studies at Brookings, Currie of Princeton University and Berger of the University of Wisconsin-Madison, write that revising the grant programs could improve the welfare of children who are at risk of abuse or neglect.
This is something else that lawmakers might consider later this year when they begin to focus on disability insurance and other programs within the Social Security law.
For Most, Social Security Is Pocket Money—Not a Pension
More than one-third of Americans who haven’t reached retirement age believes that Social Security will be a major source of income in their post-work years despite the ongoing funding problems of the government program.
The 36 percent of those polled in a recent Gallup survey who expect to rely heavily on Social Security represents the highest percentage in 15 years. It’s also nearly 10 percentage point higher than a decade ago.
Related: 6 Popular Social Security Myths Busted
In addition, 48 percent told Gallup that they expect Social Security to be a minor source of retirement funds, while only 14 percent said that they don’t expect Social Security to be a source of retirement income at all.
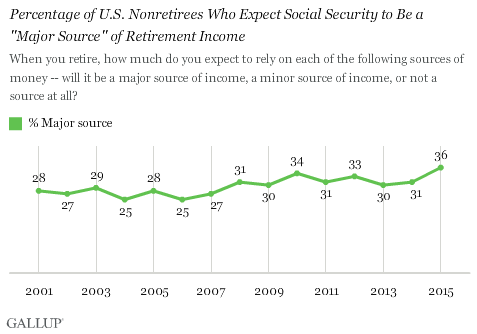
“Generally speaking, the older non-retirees are and the lower their household income is, the more they expect to rely on Social Security as a major source of retirement funds,” according to Gallup.
Close to half of non-retirees whose annual household income is less than $30,000 said Social Security will be a major source of funds.
Believing that Social Security will be a major source of retirement income might not be a great idea.
Social Security currently provides average benefits of about $1,260 a month. Going forward, Social Security checks could shrink if funding problems persist or benefits could start kicking in at an older age.
Work-Life Balance: Why Millennials Get Hit Hardest

Even with (or maybe because of) the proliferation of apps and technology to help workers connect with their jobs round-the-clock, finding a balance between work and life is getting harder, according to a new report from Ernst & Young.
The study finds that about half of managers worldwide work more than 40 hours a week, and 40 percent say their hours have increased over the past five years. In addition to technology shifts, the “always on” work culture reflects lingering effects of the recession that has left fewer employees handling larger workloads.
The balancing act is particularly difficult for millennials, who are becoming managers just as they enter into parenthood. U.S. millennial parents are the most likely to have a spouse that’s also working at least full-time, and they’re the less likely than older generations to have taken a career break when having children.
Related: 10 Easy Ways to Improve Your Work-Life Balance
More than one in four millennials is working more after having children, compared to 13 percent of Gen Xers and 16 percent of boomers. Millennial parents place a high value on flexibility, and say that a flexible schedule would make them more engaged, less likely to quit, and more likely to work flexible hours. Even so, one in six says they have suffered a negative consequence for working a flexible schedule.
More than half of those surveyed said that they would make job and career changes in order to find a better work-life balance. Those findings echo the results of a CareerBuilder survey released last year which found that a third of workers don’t want a leadership role because they don’t want to sacrifice work-life balance.
GOP Governor Asks Voters to Raise Their Own Taxes
Michigan voters go to the polls today to vote on Proposal 1, a referendum that would hike the state sales and gasoline taxes. An unexpected twist in the story, though, is who is backing the plan and why. Support for the proposal speaks to the declining state of infrastructure in the U.S. and the increasing urgency with which states are taking matters into their own hands.
Proposal 1 is a complex mix of policy changes that would raise more than a billion dollars to fund road construction and repair, plus hundreds of millions for education and other purposes. It would do so by hiking the Michigan state sales tax from 6 percent to 7 percent. That represents a 17 percent increase in total sales taxes Michiganders will face on taxable items.
Related: America’s Energy Infrastructure in Desperate Shape
However, the bill also abolishes the sales tax on gasoline – Michigan is one of the few states in which gas is not exempt from state sales tax – and would dramatically increase the wholesale gasoline tax. The net effect, according to the Detroit Free Press, would be an increase of between 7 and 9 cents per gallon in what consumers pay at the pump. The proposal would net about $1.9 billion per year for the state’s coffers, the majority of it coming out of the pockets of Michigan’s taxpayers. (A small percentage would come from out-of-state visitors paying taxes on items purchased in Michigan.)
Normally, a $2 billion tax hike – the biggest in the state in a generation – would be the sort of thing Republican politicians would attack mercilessly, but in Michigan, Republican Governor Rick Snyder is a strong proponent of the deal. And Snyder isn’t alone. Prominent Republican and Democratic lawmakers have thrown their support behind the measure.
Related: Get Ready to Pay More Tolls If Infrastructure Isn’t Funded
The move also has significant support from the business community. Unsurprisingly, the biggest backers of the deal are the construction companies and related industries. But there is also support in the general business community, even among some companies whose products would be more expensive.
Even with substantial support from legislative leaders and businesses, though, the prospects for Proposal 1 looked poor heading into the vote today Public opinion remains generally against the proposition despite a multimillion-dollar advertising campaign by supporters that has dwarfed efforts by the opposition.
Should the vote fail, though, the state’s pothole-pocked roads and crumbling bridges won’t fix themselves, so legislators will have to find the revenue somewhere, either by increasing taxes via a different route, or cutting spending from an already tight state budget.
Tequila’s Stunning Rise: How It Shot Up in U.S. Popularity

Americans are drinking more and better-quality tequila, and not only in margaritas on Cinco de Mayo.
Tequila sales have been growing at an average rate of 5.6 percent a year since 2002, according to February figures from the Distilled Spirits Council of the United States. In 2014 alone, 13.8 million nine-liter cases were sold.
Related: U.S. Surpasses France As Biggest Wine Market
The U.S. represents tequila’s largest market, with about 52 percent of global sales. America’s renewed thirst for mixed cocktails has been a boon for spirits overall, but especially for tequila. Meanwhile, sales in Mexico have remained flat largely because the market there is mature, with little room for growth.
The Distilled Spirits Council said that one of the keys to tequila’s U.S. growth has been distillers’ ability to offer a product for every budget and occasion, but the fastest growth has been in high-end and super-premium brands.
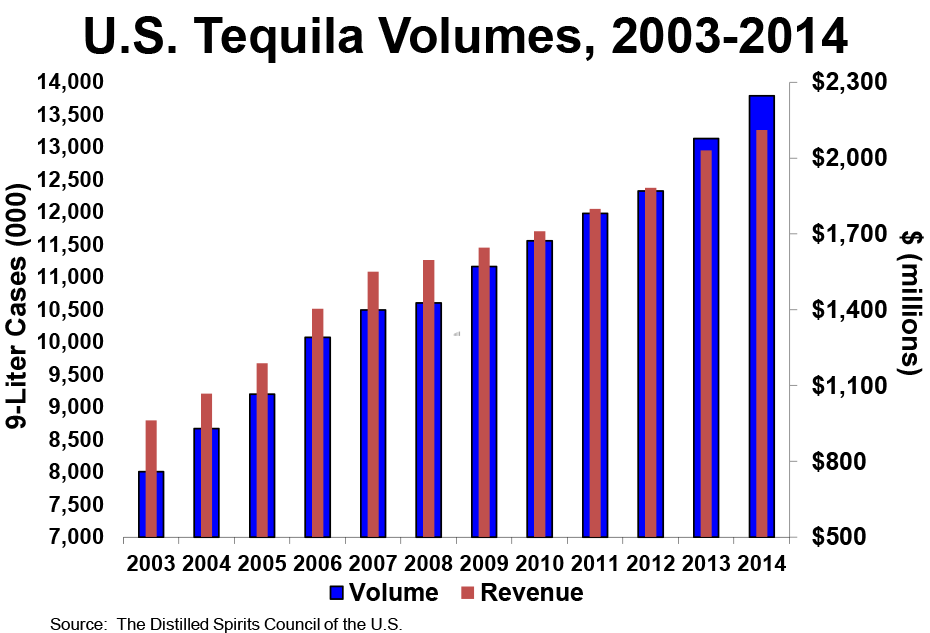
“High-end brands have grown 189 percent in volume since 2002,” it noted. “Virtually unknown in 2002, super-premium tequila volumes have skyrocketed 568 percent and today account for 2.4 million 9-liter cases.”
Celebrity endorsements may have also raised the status of tequila. George Clooney, Sean Combs and Justin Timberlake have all promoted tequila brands.
In addition, distillers are trying to boost the popularity of high-end tequilas further by offering tastings and tours — at least one of which is aimed at the super-wealthy.
Tequila Avion, an ultra-premium tequila maker, is offering a $500,000, three-day trip for 10 to Jalisco, Mexico, to taste its spirits and partake of luxury accommodations, butler service and a private dinner among other amenities.
Related: Kentucky’s McConnell and Paul Offer Tax Breaks for Bourbon
If that seems a tad pricey, Experience Tequila in Portland, Ore., offers four-day tours to Mexico for just under $1,500, and you can find tequila-tasting classes in many cities for about $100.




