Trump Diverting $3.6 Billion from Military to Build Border Wall

The Department of Defense has approved a plan to divert $3.6 billion to pay for the construction of parts of President Trump’s border wall, Defense Secretary Mark Esper said Tuesday. The money will be shifted from more than 100 construction projects focused on upgrading military bases in the U.S. and overseas, which will be suspended until Congress provides additional funds.
In a letter addressed to Senator James Inhofe, chair of the Armed Services Committee, Esper said that in response to the national emergency declared by Trump earlier this year, he was approving work on 11 military construction projects “to support the use of armed forces” on the border with Mexico.
The $3.6 billion will fund about 175 miles of new and refurbished barriers (Esper’s letter does not use the term “wall”).
Esper described the projects, which include new and replacement barriers in San Diego, El Paso and Laredo, Texas, as “force multipliers” that, once completed, will allow the Pentagon to redeploy troops to high-traffic sections of the border that lack barriers. About 5,000 active duty and National Guard troops are currently deployed on the border.
Months in the making: Trump’s declaration of a national emergency on the southern border on February 15, 2019, came in the wake of a showdown with Congress over funding for the border wall. The president’s demand for $5.7 billion for the wall sparked a 35-day government shutdown, which ended when Trump reluctantly agreed to a deal that provided $1.375 billion for border security. By declaring a national emergency, Trump gave the Pentagon the legal authority to move billions of dollars around in its budget to address the purported crisis. Legal challenges to the emergency declaration are ongoing.
Conflict with lawmakers: Congress passed a resolution opposing the national emergency declaration in March, prompting Trump to issue the first veto of his presidency. Democrats on the House Appropriations Committee reiterated their opposition to Trump’s move Tuesday, saying in a letter, “As we have previously written, the decision to take funds from critical military construction projects is unjustified and will have lasting impacts on our military.”
Majority Leader Steny H. Hoyer was more forceful, saying in a statement, "It is abhorrent that the Trump Administration is choosing to defund 127 critical military construction projects all over the country … and on U.S. bases overseas to pay for an ineffective and expensive wall the Congress has refused to fund. This is a subversion of the will of the American people and their representatives. It is an attack on our military and its effectiveness to keep Americans safe. Moreover, it is a political ploy aimed at satisfying President Trump's base, to whom he falsely promised that Mexico would pay for the construction of an unnecessary wall, which taxpayers and our military are now being forced to fund at a cost of $3.6 billion.”
A group of 10 Democratic Senators said in a letter to Esper that they “are opposed to this decision and the damage it will cause to our military and the relationship between Congress and the Department of Defense.” They said they also “expect a full justification of how the decision to cancel was made for each project selected and why a border wall is more important to our national security and the well-being of our service members and their families than these projects.”
Politico’s John Bresnahan, Connor O'Brien and Marianne LeVine said the diversion will likely be unpopular with Republican lawmakers as well. Republican Senators Mike Lee and Mitt Romney expressed concerns Wednesday about funds being diverted from their home state of Utah. "Funding the border wall is an important priority, and the Executive Branch should use the appropriate channels in Congress, rather than divert already appropriated funding away from military construction projects and therefore undermining military readiness," Romney said.
The Pentagon released a list of construction projects that will be affected late on Wednesday (you can review a screenshot tweeted by NBC News’ Alex Moe here).
An $8 billion effort: In addition to the military construction funds and the money provided by Congress, the Trump administration is using $2.5 billion in drug interdiction money and $600 million in Treasury forfeiture funds to support the construction of barriers on the southern border, for a total of approximately $8 billion. (More on that here.)
The administration reportedly has characterized the suspended military construction projects as being delayed, but to be revived, those projects would require Congress approving new funding. House Democrats have vowed they won’t “backfill” the money.
The politics of the wall: Trump has reportedly been intensely focused on making progress on the border wall, amid news that virtually no new wall has been built during the first two and a half years of his presidency. Speaking to reporters at the White House Wednesday, Trump said that construction on the wall is moving ahead “rapidly” and that hundreds of miles will be “almost complete if not complete by the end of next year … just after the election.”
6 Traits of an Emerging Millionaire: Are You One?

It’s not just Wall Street bankers, hedge fund traders and corporate raiders who will join the one percent. Nope. By now you may have heard that the new look of affluence in America is kind of… girly. The 7th Fidelity Millionaire Outlook found that today’s emerging high rollers are 66 percent female and 25 percent non-white.
The Fidelity Outlook identified 6 wealth-building traits that multi-millionaires have in common: Their starting point—a mere $250,000 in assets.
Related: Americans Are About to Get a Nice Fat Pay Raise
1 Time Horizon: On average, emerging affluent investors are just 40 years of age with 27 years left before they reach the normal retirement age of 67. Only one percent of the emerging affluent is retired.
2. Career: Many of the emerging affluent have pursued similar professions to today’s millionaires, including information technology, finance and accounting. While they might be at lower-level positions than millionaires, they have a number of years in front of them to move up the ladder.
3. Income: At $125,000, the median annual household income for the emerging affluent is 2.5X the median U.S. household income8 and is nearing the income of today’s millionaires ($200,000 for those still employed).
Related: The 10 Best States for Taxes in 2015
4. Self-Made Status: Approximately eight in 10 emerging affluent investors have earned or increased their assets on their own, a trait they share with millionaires and deca-millionaires.
5. Long-Term Focus: The emerging affluent share millionaires’ long-term focus, with three in four of both groups focused on the long-term growth of their assets, and three in 10 focused on supporting the lifestyle they want in retirement.
6. Investing Style: Similar to deca-millionaires, the emerging affluent display a willingness to invest aggressively to help maximize returns, as well as a willingness to set aside a significant portion of their portfolio for riskier investments that promise a bigger payoff. The emerging affluent and deca-millionaires were also most likely to describe themselves as “self-directed” investors, seeking hands-on involvement with their investments.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The 10 Worst States For Paying Taxes
- 6 Popular Social Security Myths Busted
- The Worst States For Retirement in 2015
Why Hard Science and Medicine Is Getting Mushy

Arthur Caplan, one of America’s top medical ethicists, is worried about pollution. Not the kind that ruins our oceans or makes it hard for us to breathe, but the kind that poses a threat to the “trustworthiness, utility, and value of science and medicine.”
Caplan, who directs the Division of Medical Ethics at NYU Langone Medical Center, wrote a blistering essay in last week’s Mayo Clinic Proceedings, saying, "The pollution of science and medicine by plagiarism, fraud, and predatory publishing is corroding the reliability of research. Yet neither the leadership nor those who rely on the truth of science and medicine are sounding the alarm loudly or moving to fix the problem with appropriate energy."
He goes on to cite three causes of publication pollution, which can undermine these areas of “hard science” that should be sacrosanct.
- The proliferation of journals that recruit authors who pay to get their articles published. Despite having substandard or no peer view, these "predatory publishers" now comprise an estimated 25 percent of all open-access journals. "Not only do they provide opportunities for the unscrupulous in academia and industry to pad their curriculum vitaes and bibliographies with bogus articles and editorial appointments, they also make it difficult for those involved in the assessment and promotion of scholars to discern value from junk," writes Dr. Caplan.
- Research misconduct, like falsifying or fabricating data or concealing serious violations. Fourteen percent of scientists report that their colleagues falsify data, and 72 percent report other questionable practices, according to one 2009 study published in PLoS One.
- Plagiarism, which, according to a 2010 Nature article was "staggering," requiring editors to spend "inordinate amounts of time" checking submissions they receive.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Biggest Outrage in Atlanta’s Crazy Teacher Cheating Case
- $45 Billion in Tax Dollars Goes Missing in Afghanistan
- How Dark Money Is Distorting Politics and Undermining Democracy
TSA Made $674,841 from Travelers’ Loose Change Last Year

That loose change in your pocket really adds up…for the government: The Transportation Security Administration collected $674,841.06 in quarters, nickels, dimes and pennies left behind by busy travelers at airport security in fiscal 2014.
In 2005, Congress allowed the TSA to put unclaimed money toward its security operations. The agency says it “makes every effort to reunite passengers with items left behind at the checkpoint, however there are instances where loose change or other items are left behind and unclaimed.” That money is turned into the TSA’s financial office.
Related: 10 Outrageous Items Confiscated by the TSA in 2014
The amount collected has been climbing each year since 2010. The 2014 total is almost $37,000 more than the agency collected the previous year and nearly $300,000 more than was left behind in 2008. In all, over the past seven years travelers have gifted the TSA $3,557,538.39.
Yes, that’s $3.5 million in spare change the agency has added to its coffers courtesy of harried travelers.
Maybe the yearly total have been climbing because travelers are increasingly engrossed with their smartphones, or maybe it’s a sign that the economy has perked up a bit so they no longer care to scoop up those nickels and dimes. Maybe it’s just that getting through a TSA checkpoint is such a hassle that travelers are willing to donate a few coins to be done with the process several seconds sooner.
Whatever the reason, here are the 20 airports where travelers left behind the most spare change in 2014:
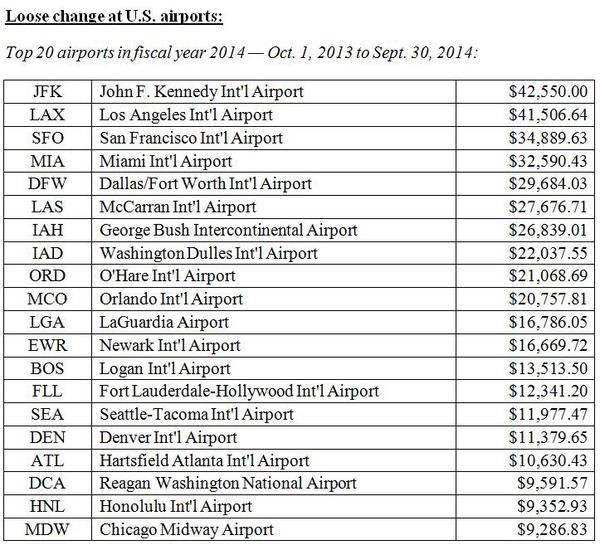
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- It Just Got Even Cheaper to Travel Overseas
- How Many Agencies Does It Take to Change a Lightbulb?
- The Government’s $125 Billion Slap in the Face to Taxpayers
Baseball in 2015: Record High Revenues

e 2015 Major League Baseball season gets underway on Monday with the sport dealing with an aging, shrinking television audience—yet league revenues, franchise valuations and player salaries are all rising faster than the stock market.
With the average MLB team now worth more than $1.2 billion and the average salary breaking $4 million, let's take a look at how the business of baseball has changed in the last few years.
A shrinking, aging television audience
"The five most-watched World Series aired in the five-year period between 1978 and 1982," said Brad Adgate of Horizon Media. All five averaged more than 38 million viewers. Contrast that with the 2014 World Series audience—a skinny 13.8 million—down 64 percent despite an increased U.S. population. Media buyer Adgate said that's "unlike the Super Bowl, which has set an audience record in five of the last six years."
Related: Madison Bumgarner: Exhibit A in Baseball’s Screwball Salary System
Not only is the audience declining, but it's aging too: Last year's World Series had a viewer with a median age of 55.6—a new high. Just five years prior, it had been sub-50 at 49.9, and was in the 44-46 range during the early 1990s.
