How IBM Is Making Your Passwords Useless
For years, quantum computing has been hailed as a technology that could change the way the modern world works, but a long-standing technical issue has kept that potential from being realized. Now, in a paper published in the journal Nature last week, IBM scientists have taken a big step (see how I avoided the temptation to make a pun there?) toward solving that problem — and while it could represent progress toward making quatum computers real, it also could mean that current cybersecurity standards will soon be much easier to crack. In other words, your passwords could be obsolete soon.
The power of quantum computing has some obvious appeal: The increase in processing power could speed up research, especially in big data applications. Problems with large datasets, or those that need many millions (or billions, or more) of simulations to develop a working theory, would be able to be run at speeds unthinkable today. This could mean giant leaps forward in medical research, where enhanced simulations can be used to test cancer treatments or work on the development of new vaccines for ebola, HIV, malaria and the other diseases. High-level physics labs like CERN could use the extra power to increase our understanding of the way the universe at large works.
But the most immediate impact for the regular person would be in the way your private information is kept safe. Current encryption relies on massively large prime numbers to encode your sensitive information. Using combinations of large prime numbers means that anyone trying to crack such encryption needs to attempt to factor at least one of those numbers to get into encrypted data. When you buy something from, say, Amazon, the connection between your computer and Amazon is encrypted using that basic system (it's more complicated than that, but that's the rough summary). The time it would take a digital computer to calculate these factors is essentially past the heat death of the universe. (Still, this won't help you if your password is password, or monkey, or 123456. Please, people, use a password manager.)
Quantum computing, however, increases processing speed and the actual nature of the computation so significantly that it reduces that time to nearly nothing, making current encryption much less secure.
The IBM researcher that could make that happen is complicated, and it requires some background explanation. For starters, while a "traditional" computing bit can be either a 0 or a 1, a quantum computing bit can have three (or infinite, depending on how you want to interpret the concept) states. More specifically, a qubit can be 0, 1, or both.
 Up until now, the both part of that caused some problems in realizing the power of quantum computing.
Up until now, the both part of that caused some problems in realizing the power of quantum computing.
Apparently — and you'll have to take this on faith a bit, as it hurts my head to think about it — the both state can switch back to either 0 or 1 at any given point, and sometimes incorrectly, based on the logic in the programming. Think about when your phone freezes up for a second or two while you're matching tiles. This is its processor handling vast amounts of information and filtering out the operations that fail for any number of reasons, from buggy code to malware to basic electrical noise. When there are only the two binary states, this is a process that usually happens behind the scenes and quickly.
The hold-up with quantum computing up until now is that the vastly greater potential for errors has stymied attempts to identify and nullify them. One additional wrinkle in this reading quantum states is familiar to anyone with basic science fiction knowledge, or perhaps just the ailurophobics. What if the action of reading the qubit actually causes it to collapse to 0 or 1?
The very smart people at IBM think they've solved this. The actual technical explanation is involved, and well beyond my ability to fully follow, but the gist is that instead of just having the qubits arrayed in a lattice on their own, they are arranged such that neighbors essentially check each other, producing the ability to check the common read problems.
That opens the door to further quantum computing developments, including ones that will make your password a thing of the past. So, does this mean that you need to start hoarding gold? No, not yet. And hopefully before quantum computing reaches commercial, or even simply industrial/governmental levels, a better cyber security method will be in place. Or the robots will have already taken over. I for one welcome them.
More Americans Have Health Insurance (Whether They Want it or Not)
The latest Gallup survey shows the rate of American adults without health insurance dipped to an all-time-low of 11.9 percent in the first quarter of this year, down from 12.9 percent at the end of 2014 and 18 percent in mid-2013. That means nearly nine in 10 adults now say they have health coverage, which Gallup attributes primarily to provisions in the Affordable Care Act.
So far, the White House estimates that more than 16 million people have gained health coverage through Obamacare.
Related: Obamacare Goes to Court as Uninsured Rate Hits New Low
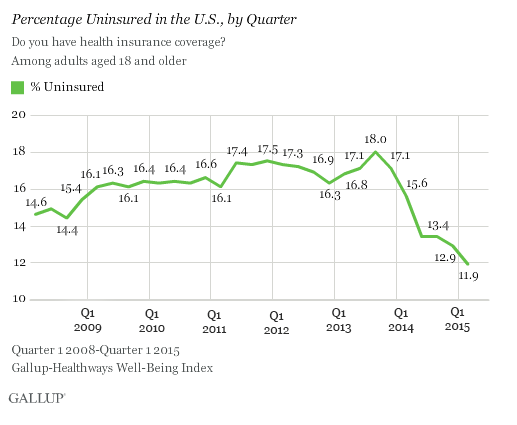
Gallup notes that the uninsured rate is likely to continue trending downward this year as more people sign up for coverage during the special enrollment period, which ends on April 30. The administration granted extra time to people who were unaware of the law’s individual mandate requiring everyone to have health coverage or be subject to a tax penalty.
The pollsters noted that there are, of course, other factors that have helped lower the percentage of uninsured people in the U.S., including the improving economy and a falling unemployment rate. Even so, they suggested that Obamacare played the largest role: “The uninsured rate is significantly lower than it was in early 2008, before the depths of the economic recession, suggesting that the recent decline is due to more than just an improving economy.”
Related: Poll Shows Why Obamacare Ruling Could Be Devastating
The poll of 43,575 adults over the first three months of the year suggests that the health care reform law is succeeding in its primary goal of expanding access to coverage, though questions remain about just how affordable that care is — and whether the law will be undone by a Supreme Court ruling, scheduled to be announced in June in the case of King v Burwell. The high court’s interpretation of language in one sentence of the Affordable Care Act will determine whether roughly 8 million people will lose health insurance subsidies. Read about the case here.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- 6 Popular Social Security Myths Busted
- The Battle Is On to Save Military Bases from Closure
- The 10 Worst Places for Obamacare in 2015
John Oliver Explains Why We Shouldn’t Hate the IRS
Everyone hates the IRS. Even the mothers of its agents hate the tax-collection agency. And that sentiment rises to new levels around this time of year.
On his HBO show last night, John Oliver said those feeling are only natural: “Is it any wonder that everyone hates the IRS?” he said. “Dealing with them is obligatory. It often functions badly. And it combines two of the things we hate most in life: someone taking our money and math.”
Still, Oliver went on to “attempt the impossible”: making viewers feel at least a smidgen of sympathy for the tax man — and explaining why our widespread hatred may be misguided. It’s Congress, after all, that writes the tax code. And it’s Congress that has made it harder for the agency to do its job by cutting the IRS budget from $13.4 billion in 2010 to $10.9 billion this year. As BusinessWeek just said in its latest cover story, "if you think paying your taxes is bad, try working at America's most unloved agency."
Related: IRS Says Budget Cuts Could Bilk Billions from Taxpayers
“I’m not saying the IRS is a likeable organization,” Oliver said. “But not everything that’s important is likeable. Think of our government as a body. The IRS is the anus. It’s nobody’s favorite part. But you need that thing working properly…”
It’s not that we should love the IRS, or even like them, Oliver said. But the agency deserves “a few minutes of at least grudging acknowledgment of the unpleasant, necessary function they serve.” And to provide that, Oliver brought on the singer who might be even more despised than IRS: Michael Bolton.
Watch the segment below (warning: it includes HBO-appropriate language):
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- IRS Struggles to Help Victims of Identity Fraud
- The Battle Is On to Save Military Bases from Closure
- Six Fascinating Facts About the Future of Religion
'Star Wars' Digital Downloads: Aren't You a Little Expensive for a 40-Year-Old Movie?

The Star Wars movies are available today for digital purchase on services like iTunes, Google Play and Amazon Instant Video for the first time. For $89.99 you can own two and a half good movies, and then hours of other stuff George Lucas also made, now featuring nine additional hours of bonus features.
That purchase price might be palatable to some fans, but seems a lot to charge as a promotional tool ahead of this December's new J.J. Abrams-directed installment in the franchise, now owned by The Walt Disney Company. Especially considering the franchise has already earned something on the order of $27 billion across its various outlets.
But most of that went directly to Lucasfilm, before Disney completed its purchase. Along with its Marvel revenues, Disney should see quite the revenue bump from the sci-fi/fantasy world this year, with The Avengers: Age of Ultron, the sequel to the third-highest grossing movie ever, opening next month, followed by Star Wars: Episode VII in November.
While there are probably some people out there who have no idea what it means to ask "who shot first?", those people are not likely to pay $90 to find out. And for those fans who do know, it seems the new digital versions still have the wrong answer.
Cavity Watch: 7-Eleven To Host 'Bring Your Own Cup' Slurpee Day

If, for some reason, you’ve ever wanted to induce a diabetic coma, tomorrow might be the time to do it.
7-Eleven, the chain of convenience stores most favored by packs of high-school layabouts who aren’t yet old enough to hang out in bars, is holding a promotion called “Bring Your Own Cup Day” tomorrow, April 11.
What is it? Glad you asked. Bring Your Own Cup Day (or #BYOC if you’re on the Twitters) is a Bacchanalian feast of excess where customers bring a watertight vessel to their nearest 7-Eleven, smack $1.50 on the counter, and fill said vessel with the Slurpee of their choosing.
Related: 10 Best Fast Food Restaurants in America
There are limitations though, so hold your hedonistic horses. Whatever container you choose to use must be non-porous, so no baseball caps or fedoras. Also, whatever container you bring must be able to fit through a 10-inch diameter hole – so put that oil drum back in the basement. Even with the size limitations, you could still be getting a deal – USA Today posits that a cup that just makes the cut could hold a gallon of 7-Eleven’s finest sugar water.
According to 7-Eleven’s VP of marketing, Laura Gordon, the event is being presented as a “Summer Kickoff,” which seems a little optimistic considering the fact that it’s foggy, 48 degrees Fahrenheit, and drizzling right now in New York City. Still, who am I to judge? Maybe the gods will look favorably upon 7-Eleven’s offering, and bring a day of sunshine, Slurpees, and nothing but syrup:
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- The Long, Slow Death of Cable Just Reached a Tipping Point
- The App-Selling Power of Kate Upton’s Cleavage
- 10 Biggest Tech Flops of the Century
Six Reasons Not To Buy an Apple Watch Just Yet

The Apple Watch is Apple's first entry into an entirely new product category in about five years, and it’s come under much scrutiny during the process of its development and unveiling. Reviewers have finally got ahold of the device and have released a glut of early evaluations. The consensus: The Apple Watch is great — definitely better than most, if not all, of its predecessors — but with some caveats potential buyers should keep in mind. Most critics so far agree that the device seems superfluous, tricky to use, and a little silly at first — but then it quickly grows on you. Reviewers like The New York Times's Farhad Manjoo, The Wall Street Journal's Joanna Stern and The Verge's Nilay Patel have extended cautious thumbs up for the product, but still warn that it’s a flawed device that may not be right for buyers just yet. Here are six reasons why the reviewers are hesitant — and perhaps you should be, too:
1. The Cost
The Apple Watch costs a pretty penny: The cheapest model clocks in at $349, with prices for fancier models going all the way up to an ultra-exclusive $17,000. At those prices, you want a device that does a lot more than look cool. “You only get a charging cable, which is lame,” Patel wrote. “For $700, you should get a nice charging stand, like you get with the $249 Moto 360. Apple makes a stand, but it only comes with the $10,000-and-up Apple Watch Edition models. Crazy.”
Watch It: As was the case with the original iPhone, the high price might be part of the appeal for some show-offs. As Joanna Stern says in her review: "After over a week of living with Apple’s latest gadget on my wrist, I realized the company isn’t just selling some wrist-worn computer, it’s selling good looks and coolness, with some bonus computer features."
Related: Apple Watch Could Be Apple’s First Major Flop This Century
2. The Learning Curve
A surprisingly common complaint was the apparent lack of out-of-the-box workability, with many reviewers claiming that it took them several days of tweaking to get things going just right. Said Manjoo: "Indeed, to a degree unusual for a new Apple device, the Watch is not suited for tech novices." Bear in mind, too, that this is an experienced tech writer who has presumably seen way more than his fair share of badly implemented devices with limited documentation, so if he had to spend time tweaking things, you can bet that your average out-of-the-box, "it just works" Apple user is going to be utterly baffled. Give it a year or so, and they'll have ironed out all the kinks and streamlined things a bit.
Watch It: Tech writers may be more critical than the average buyer, and less wowed by Apple’s cool factor. Early adopters in particular may be willing to scale the learning curve while Apple makes improvements for next generations of the Watch.
3. Battery Life Should Be Better
The Watch is on your wrist — it's always there and is intended to consistently be in use — but reviewers have found that the Apple Watch’s charge ran low after a day of heavy use. Stern’s barely managed to last the course of a full day, and that was while leaning on its "power saving mode," which cut features and dimmed the backlight. “Do you want another tiny computer in your life that you have to worry about and charge every day?” Patel asked.
Watch It: Hey, how often do you charge your smatphone? Is it such a big deal to plug in the device at night while we all wait for battery life to improve across all our devices?
Related: 10 Biggest Tech Flops of the Century
4. It's Painfully Slow
Here’s how Patel at The Verge summed it up: "There’s no getting around it, no way to talk about all of its interface ideas and obvious potential and hints of genius without noting that sometimes it stutters loading notifications. Sometimes pulling location information and data from your iPhone over Bluetooth and Wi-Fi takes a long time. Sometimes apps take forever to load, and sometimes third-party apps never really load at all. Sometimes it’s just unresponsive for a few seconds while it thinks and then it comes back."
Watch It: Apple has already claimed that it will be releasing a series of updates to address these issues. Of course, future generations of the Watch will undoubtedly come with hardware improvements as Moore's Law threatens to overtake us all.
5. It's Not Yet Ubiquitous Enough to Be Needed
The marketing of the Apple Watch frames it as a time-saving panacea: Swipe it at an Apple Pay-enabled checkout counter and complete your purchase without having to whip out your wallet; tap it against a hotel room door to gain entry without fussing with a keycard; or hail an Uber with a quick wrist-call to Siri. The thing is, none of those things have been put in place yet, at least not on a universal scale, so for now the Watch mainly serves to tell the time, browse Twitter, check e-mails and remind you of appointments. There are plenty of other devices that can handle that in the interim.
Watch It: Much like the slow takeover of the smartphone, though, we'll probably see an increased adoption of the technology as developers scope out the market and adoption grows. Have you checked out the App Store lately?
Related: What the Apple Watch Will Do for Apple
6. The Backlash
It's the curse that befalls all early adopters in the wearables industry: No matter how cool or slick a product may be, it’s kinda hard to wear out in public without attracting stares. Early adopters of Google Glass faced similar issues, becoming the unfortunate targets of the derogatory pseudonym "Glassholes." When the day-one fanboys start sitting on public transit, talking into their wrists like a low-budget Dick Tracy, it's hard to imagine they won't come under some kind of ridicule. If you think you can handle a bit of mockery and attention, more power to you.
Watch It: First off, Apple has made a concerted effort to make the Watch as aesthetically pleasing as possible at all points along the price spectrum. Second, those stares and questions are part of the appeal for some buyers. And even if you aren’t looking for added attention, it might not be long before the Apple Watch just becomes part of our everyday scenery. How many people are still asking to look at your iPhone 6 Plus?
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- The App-Selling Power of Kate Upton’s Cleavage
- 15 of the Most Valuable Beanie Babies
- Americans Are About to Get a Nice Fat Pay Raise
