The Kids Aren’t Alright: More Millennials Are Living with Their Parents

Pity the millennial, poster child of the Great Recession. A popular meme portrays the typical millennial as a basement-dwelling economic loser, forever condemned to live in the nether regions of his parent’s house. Unfortunately, that meme is not without basis. The recession seem to have hit millennials particularly hard, making it even more difficult for young people to find good jobs and to establish their own households.
In some respects, things are looking up for millennials. The U.S. job market is strengthening, making it easier to find work, and wages are starting to creep higher. The unemployment rate for young adults (ages 18 to 34, excluding full-time college students) has been heading lower since peaking near 12 percent in 2010; the latest unemployment reading for millennials is 7.7 percent.
However, there is one notable sticking point, and it echoes that basement-dwelling meme. Even though household formation rates have rebounded overall, millennials are still not moving out and establishing their own households like they used to. In fact, more millennials are living with parents or relatives than before the recession, according to new research from Pew.
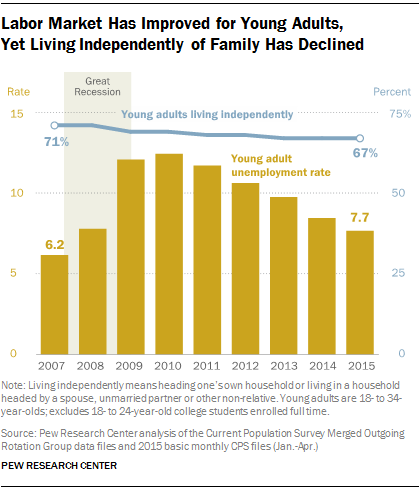
In 2007, before the recession hit, 71 percent of millennials were living independently. In 2015, that number has fallen to 67 percent, with no sign of bottoming.
On the flip side, 22 percent of young adults were living in their parents’ homes in 2007. That number has risen to 26 percent this year.
The Pew report doesn’t look at why millennials are sticking so close to home. However, it does suggest that the relatively simple economic argument about the lack of good jobs no longer tells the whole story. Since the economy is recovering, however unevenly, there are likely other factors in play. One could be cultural: More young people simply enjoy living at home and are in no hurry to move out. Perhaps the U.S. is becoming more like Italy, where adult children often live at home until they marry.
That’s not to say that money plays no role in the trend, though. One big economic factor not addressed in the Pew report is pretty basic: rising rents. This graphic from Zillow makes it clear that rents have been soaring all over the country. More than $3,000 for a one bedroom in San Francisco? With those kind of numbers, living at home makes all the sense in the world.
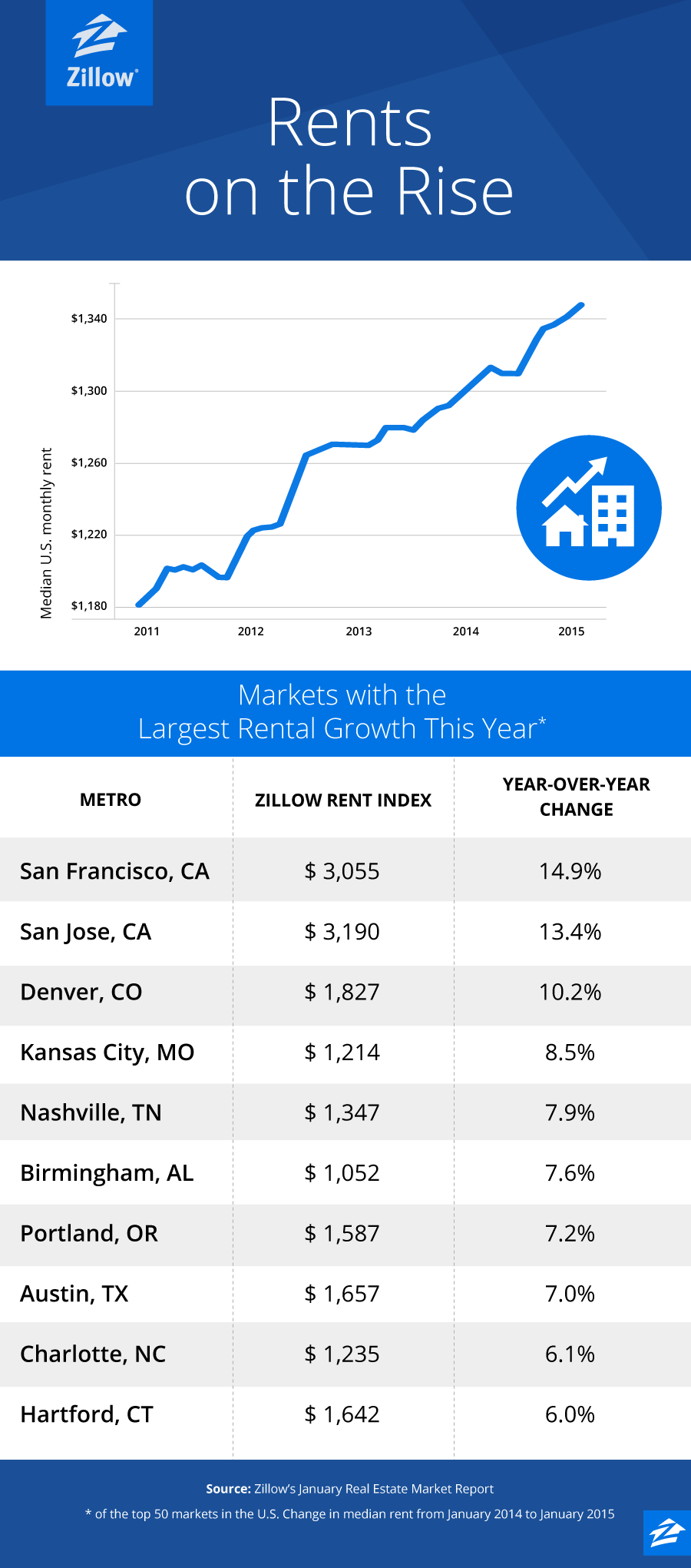
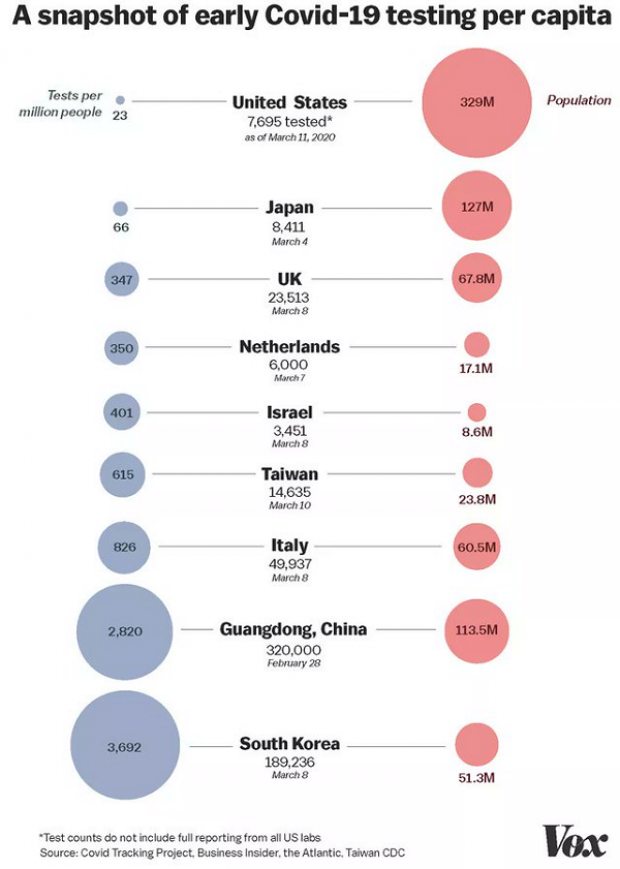
Chart of the Day: Long Way to Go on Coronavirus Testing

The White House on Friday unveiled plans for a new effort to ramp up testing for Covid-19, which experts say is an essential part of limiting the spread of the virus. This chart from Vox gives a sense of just how far the U.S. has to go to catch up to other countries that are dealing with the pandemic, including South Korea, the leading virus screener with 3,692 tests per million people. The U.S., by comparison, has done about 23 tests per million people as of March 12.
After Spending $2 Billion, Air Force Bails Out on Planned Upgrades of B-2 Bombers

The Air Force has scrapped a planned upgrade of its B-2 stealth bomber fleet — even after spending $2 billion on the effort — because defense contractor Northrup Grumman didn’t have the necessary software expertise to complete the project on time and on budget, Bloomberg’s Anthony Capaccio reports, citing the Pentagon’s chief weapons buyer.
Ellen Lord, the undersecretary of defense for acquisition and sustainment, told reporters that the nearly $2 billion that had already been spent on the program wasn’t wasted because “we are still going to get upgraded electronic displays.”
Big Hurdle for Sanders’ Plan to Cancel Student Debt

Bernie Sanders wants to eliminate $1.6 trillion in student debt, to be paid for by a tax on financial transactions, but doing so won’t be easy, says Josh Mitchell of The Wall Street Journal.
The main problem for Sanders is that most Americans don’t support the plan, with 57% of respondents in a poll last fall saying they oppose the idea of canceling all student debt. And the politics are particularly thorny for Sanders as he prepares for a likely general election run, Mitchell says: “Among the strongest opponents are groups Democrats hope to peel away from President Trump: Rust Belt voters, independents, whites, men and voters in rural areas.”
Number of the Day: $7 Million

That’s how much Michael Bloomberg is spending per day in his pursuit of the Democratic presidential nomination, according to new monthly filings with the Federal Election Commission. “In January alone, Bloomberg dropped more than $220 million on his free-spending presidential campaign,” The Hill says. “That breaks down to about $7.1 million a day, $300,000 an hour or $5,000 per minute.”