Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
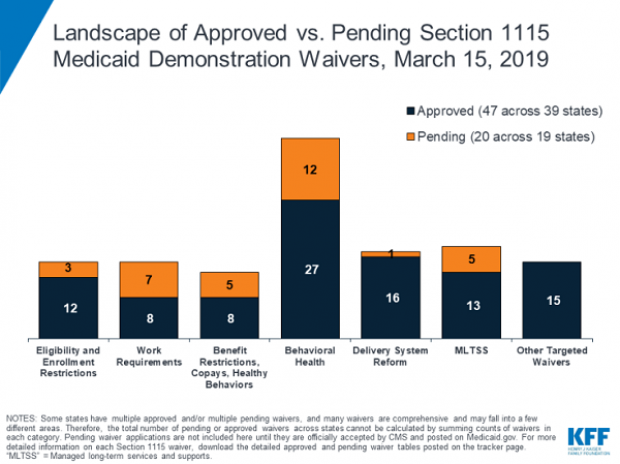
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
A Military Coup in the U.S.? A Surprising Number of Americans Might Support One

Imagine you’re watching the evening news, kicking back after a long day in the cubicle. Suddenly a breaking news alert flashes across the screen: “Military Coup Overthrows the Government.” What would be your reaction?
While most Americans say they can’t imagine supporting a takeover of the government by the armed forces, or least aren’t sure about it, a substantial number of people say they can imagine supporting the military in such a scenario.
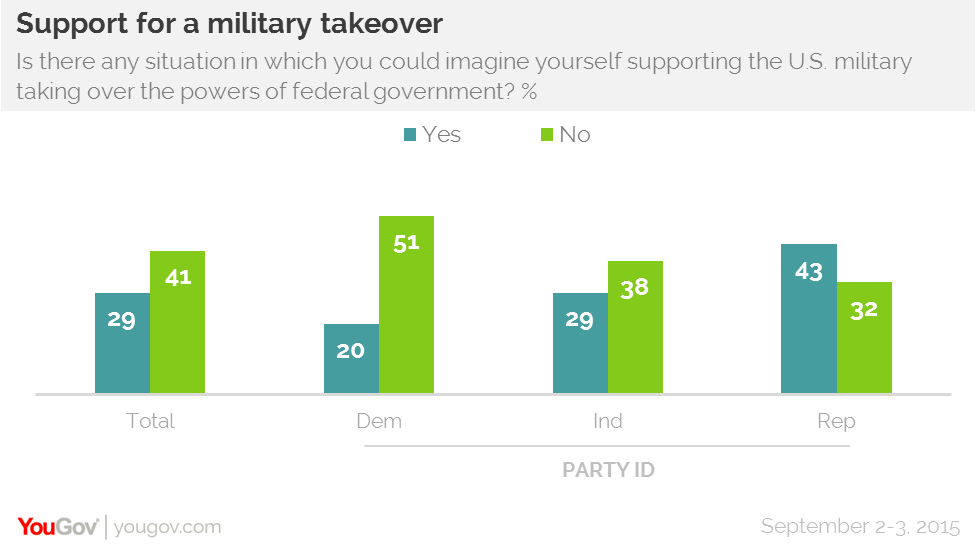
In a new survey by YouGov, 29 percent of respondents said they can imagine a situation in which they would support the military taking control of the federal government – that translates into over 70 million American adults. Forty-one percent of respondents said could not imagine supporting the military taking over the country.
Related: With $8.5 Trillion Unaccounted for, Why should Congress Increase the Defense Budget?
Republicans (43 percent) were more likely to say they can envision a scenario in which they could support a military coup than Democrats (20 percent). Perhaps that difference is related to having a Democratic president who some critics on the right see as overstepping his power.
Regardless of political ideology, one reason people might support a military coup is because they respect officers in the military far more than they do people in Congress. According to the same YouGov survey, almost three-quarters (70 percent) of respondents believe that military officers want what is best for the country, while only 29 percent think the same of members of Congress.
Lawmakers better shape up or they might be shipped out -- literally.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- A Conservative Rebellion is Brewing on Capitol Hill
- 9 ISIS Weapons That Will Shock You
- There’s Only One Candidate People Actually Like – and It’s Not Trump or Clinton
Sanders Pulls Ahead in Iowa, but a Tougher Clinton Aims to Even the Score

A new poll unveiled Thursday finds populist Bernie Sanders squeezing past Hillary Clinton for the first time as the preferred choice among likely Iowa caucus-goers.
The survey by Quinnipiac University shows the Vermont lawmaker receiving 41 percent, while Clinton garnered 40 percent. The figures put Sanders’ lead well within the poll’s 3.4 percent margin of error, but the numbers serve as another indication of how tight the Democratic primary has become, especially in Iowa where Clinton has long maintained an advantage.
Related: With Trump and Sanders Riding High, How Low Will Bush and Clinton Go?
The poll found another 12 percent of voters would support Vice President Joe Biden, who has yet to decide if he will enter the 2016 race. Former Maryland Governor Martin O’Malley received 3 percent, and the same number were undecided.
While many could view the survey as the latest sign Clinton’s campaign is flailing, the timing of the poll could prove crucial.
The study was conducted between August 27 and September 8. That was the same day the former secretary of State told ABC News that using a personal email account while in office was a mistake and that she is sorry for it.
Related: Hillary’s E-Mail Lapse ... Mistake ... Responsibility ... er, 'Apology'
“I do think I could have and should have done a better job answering questions earlier. I really didn’t perhaps appreciate the need to do that,” Clinton said. “What I had done was allowed, it was above board. But in retrospect, as I look back at it now, even though it was allowed, I should have used two accounts. One for personal, one for work-related emails. That was a mistake. I’m sorry about that. I take responsibility.”
The interview marked the first time she apologized for her unique email arrangement. Questions over Clinton’s use of a private server have dogged her candidacy since she entered the White House race earlier this year.
Republicans have used the controversy surrounding the server to paint Clinton as untrustworthy and unfit to serve in the White House.
Related: Clinton: Trump Is Bad for American Politics
Indeed, Thursday’s poll found that while Clinton is still liked among Democratic voters who believe she would make a good leader, Sanders fares better on the question of trustworthiness.
The Quinnipiac poll also closed before Clinton gave a muscular foreign policy speech at the Brookings Institution on, among other things, the Iran nuclear deal.
“We should anticipate that Iran will test the next president,” she said. “They'll want to see how far they can bend the rules.”
“That won't work if I'm in the White House. I'll hold the line against Iranian noncompliance,” Clinton added.
On the softer side of things, Clinton’s interview on “The Ellen DeGeneres Show” will air Thursday afternoon. The appearance will give her a chance to connect with female voters who are the backbone of her support.
Taken together, the various actions could put Clinton back atop the polls, at least in Iowa, and help her gain back ground she lost to Sanders in New Hampshire as well.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times:
- House GOP Scores a Major Win in Obamacare Legal Challenge
- Hillary’s E-Mail Lapse ... Mistake ... Responsibility ... er, 'Apology'
- How Can You Tell There Are Russian Troops in Syria? Just Look for Some Soldier Selfies
College Students Say They’re Good with Money. Do You Believe Them?

A new study confirms it: College students think they know everything, at least when it comes to personal finance.
Nearly 60 percent of college students said that they had good or excellent financial literacy skills, according to a study released today by the American Institute of CPAs.
Despite that confidence, less than half of students say they stick to a monthly budget, nearly 40 percent had borrowed money from friends or family and more than 10 percent had missed a bill payment.
Of those surveyed, 99 percent said that personal financial management skills were important, but only a quarter said they seek out information on personal finance and incorporate it into their spending and saving habits.
“For many students, college is their first time making financial decisions,” Ernie Almonte, chairman of the AICPA’s Financial Literacy Commission said in a statement. “With this opportunity comes serious responsibility, and if they aren’t making informed, intelligent decisions it can have a negative impact on the rest of their financial lives.”
College students without a strong foundation in personal finance are more likely to take on risky debt or make poor saving decisions. But most students aren’t getting the education they need before they get to campus.
Just 17 states require high school students take a personal finance course, and only six require testing of personal finance concepts, according to the Council for Economic Education. Three out of four American teens can’t even make sense of a paystub.
But hey, at least they’re confident.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- House GOP Scores a Major Win in Obamacare Legal Challenge
- Hillary’s E-Mail Lapse ... Mistake ... Responsibility ... er, 'Apology'
- How Can You Tell There Are Russian Troops in Syria? Just Look for Some Soldier Selfies
How Can You Tell There Are Russian Troops in Syria? Just Look for Some Soldier Selfies

Although Russian President Vladimir Putin has denied that he is sending troops to Syria, selfies taken by Russian soldiers and posted on social media are telling a different story.
Russian investigative journalist Ruslan Leviev reports that an increasing number of experienced Russian troops have been deployed to a naval maintenance facility in Tartus, along Syria’s Mediterranean coast. His source? Status updates and photos posted on Russia’s two biggest social networking sites by members of the 810th marine brigade, an infantry force in the Russian navy.
Related: As Putin Targets Dissent, U.S. Democracy Group Banned in Russia
One photo Leviev found is of a career soldier named Mazhnikov, who appears to be at the naval facility in Syria. Another soldier, Anatoly Golota, also a member of the 810th brigade, updated his status on the Russian version of Facebook with the words, “Off to Syria :)).”
Russia has not denied that it’s been supplying weapons to the Syrian government and helping train the Syrian military. But Putin knows that combat troops are a different story.
The naval maintenance facility at Tartus is small, and in the past has been manned by just a handful of personnel. Leviev reports that the number of troops stationed at the facility is growing, and the troops are experienced contract soldiers, not draftees.
Videos uploaded to social media sites have raised concerns that Russian troops might be involved in combat inside Syria, according to an article in Foreign Policy. However, beyond the footage, which shows a Russian-made BTR-82A armored vehicle firing its gun in Syria, no other substantial evidence of active combat involving Russian troops has been found.
While the marines may or may not be directly involved in the fighting, the presence of Russian troops in Syria shows how hard Putin is pressing for a victory by the Assad regime. Now if he can just teach his soldiers how to avoid giving themselves away on social media.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- Putin’s Economy May Be in Even Worse Shape Than It Looks
- China Sends a Message with Its New ‘Carrier Killer Missile
- In Showing Off Physical Strength, Putin Tries to Hide Political Weaknesses
Americans Just Went on a $32 Billion Credit Card Shopping Spree

Americans may be heading for another credit card crunch. After paying down almost $35 billion in credit card debt in the first quarter of the year, consumer charged up a storm in the second quarter, racking up $32.1 billion in new debt, according to CardHub, a credit card comparison site. CardHub says that’s the second highest quarterly total since it began keeping data on credit card debt in 2009.
While that buying binge could potentially signal improved confidence in the economy and in their own financial prospects, CardHub warns that the debt risks are building. It projects that consumers will close out the year with an annual net increase of more than $60 billion in credit card debt, with the total credit card debt outstanding climbing to more than $900 billion, the highest since the recession.
Related: 5 Cities with the Most Credit Card Debt
CardHub CEO Odysseas Papadimitriou says that jump brings Americans “perilously close to a tipping point at which balances become unsustainable and delinquency rates skyrocket.”
For 7 out of the past 10 quarters, consumers have racked up more debt than they’ve paid off. Papadimitriou cites that as evidence that consumers are going back to the bad habits they had before the economic downturn.

CardHub based its study on data from the Federal Reserve, and if the results are a sign of trouble then another new report from the Federal Reserve Bank of New York suggests that problem is even worse than it looks. In a report called “Do We Know What We Owe,” the New York Fed found that people widely underestimate their credit card debt, telling the Fed’s survey-takers that it’s about 37 percent lower than what lenders say it is.
So if we are actually getting to a tipping point with credit card debt, it may be even closer than we realize.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- Millions Facing a Hefty Increase in Medicare Premiums in 2016
- How Much Does Our Social Safety Net Cost? $742 Billion a Year and Rising
- The 10 Worst States for Property Taxes