Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
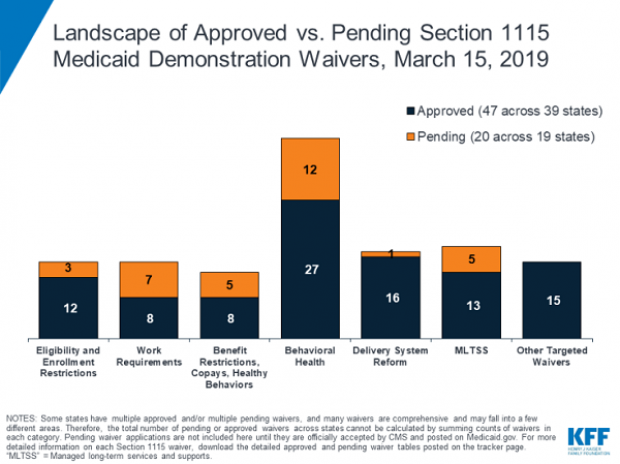
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
The Surprising Reason for the Boom in Snack Sales

Americans are increasingly dining alone, and they’re opting for snacks rather than full meals, according to a new report from NPD group.
A key driver of the trend is the growing number of single-person households, since solo eaters are more likely to opt for snack foods for dinner. Nearly a quarter of all snack foods consumed last year were consumed at mealtime.
“Smaller household sizes and eating alone are among the growing factors with snacking,” NPD food and beverage industry analyst Darren Seifer said in a statement. “Food manufacturers should think about the unique needs of the solo consumer when developing products and packaging, and marketing messages should be crafted to be relevant to them and their snacking behaviors.”
Related: The 12 Hottest Food Trends for 2015
A separate report released by Nielsen last year found that more than half of global diners had selected snacks in the past 30 days to replace a lunch, 48 percent had snacked for breakfast and 41 percent had snacked for dinner.
When making their selection, single diners prefer single-serve packages and are increasingly turning to “better-for-you” snacks, like fresh fruit, breakfast bars, and yogurt, NPD found.
Food manufacturers are starting to adapt to the demand for healthier options. In June, General Mills said it would stop using artificial colors and flavors by 2016, and Kellogg Co. has vowed to do so by 2018.
Even as demand grows for healthier snacks, the most popular snacks in North Americans might make a nutritionist cringe. Nielsen found that the most popular snacks were chips, followed by chocolate and cheese.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- The $1 Trillion Question for the F-35: Is the U.S. Buying an Inferior Plane?
- Hillary’s College Plan—Debt Free College Now, Tax Them When They Make Money
- You Won’t Believe What Some Job Seekers Are Putting on Their Resumes
Obamacare Drives Uninsured Rate to Record Low

With the number of Americans lacking health insurance in decline, the rate of uninsured Americans has hit a record low, reaching levels not seen since the National Center for Disease Statistics began keeping records in 1972.
In the first quarter of 2015, 9.2 percent of all Americans were uninsured, according to new data from the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, down from 11.5 percent in 2014. The total number of uninsured Americans fell by 7 million over the past year, from 36 million in 2014 to 29 million in the first three months of 2015.
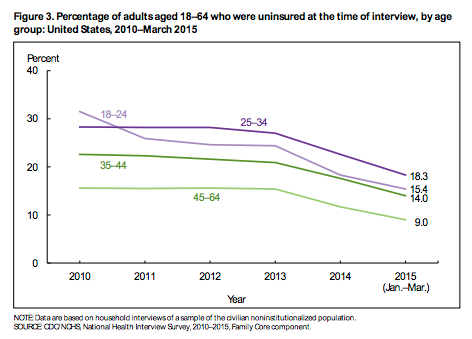
The largest declines were seen among adults who were poor or near-poor, suggesting that the Affordable Care Act was responsible for the most significant gains in coverage. Both groups dropped from uninsured rates near 50 percent in 2010 to 28 percent among poor adults and 23.8 percent among near-poor adults in 2015.
While Democrats are citing data as evidence that the Affordable Care Act is working, Republicans will likely argue that the reduction is being driven by an improving economy and a steadily declining unemployment rate.
Arkansas and Kentucky continue to record the most noticeable reductions in uninsured rates since Obamacare took effect at the beginning of 2013, according to a new report by Gallup. Texas is the only state to still have an uninsured rate higher than 20 percent.
We Built a $335 Million Power Plant in Afghanistan that Can Barely Turn on Lightbulb

USAID is denying that a $335 million “vital component” of their mission to aid the massive energy deficit in Kabul, Afghanistan is an utter failure, but a new report contradicts that claim.
A power plant built by U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) is extremely underused and in danger of being wasted, according to the Special Inspector General for Afghanistan Reconstruction (SIGAR). USAID attempted to defend itself by saying the plant was only built to provide occasional backup and insurance for Kabul’s electrical grid, not for electrical power on a continuous basis. SIGAR’s report provides evidence that the plant was built for regular usage.
Related: U.S. Military Builds a $15 Million Warehouse That Nobody Wants
First, the basis of design was for a base load plant, built to operate 24 hours per day, 7 days a week. Also, the plant hasn’t made any impact on reducing Kabul’s massive energy deficit that USAID says is one of the plant’s main priorities. Not only is it not being used regularly, but it’s not even contributing additional electricity to increase the overall power supply in Kabul.
The Tarakhil Power Plant was built in July 2007 on the outskirts of Kabul, with the intention of supplying 18 diesel engines worth of operating power. Since Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) – Afghanistan’s national power utility – assumed responsibility for the operation and maintenance of the facility in 2010, the plant has only performed at a shred of its total capability. Between July 2010 and December 2013, the USAID IG found that the plant performed at a mere 2.2 percent of its potential.
Since the Tarakhil Power Plant was used incorrectly and only on an intermittent basis, the plant has suffered premature wear and tear on its engine and electrical components. The damage is expected to raise already steep operation and maintenance costs.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- How ‘King Coal’ Could Swing the 2016 Election
- Kerry to Congress: Sign the Iran Deal or the Dollar Gets Hit
- China’s Currency Devaluation Brings Stocks to a 'Death Cross'
We Built a $335 Million Power Plant in Afghanistan that Can Barely Turn on Lightbulb

USAID is denying that a $335 million “vital component” of their mission to aid the massive energy deficit in Kabul, Afghanistan is an utter failure, but a new report contradicts that claim.
A power plant built by U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) is extremely underused and in danger of being wasted, according to the Special Inspector General for Afghanistan Reconstruction (SIGAR). USAID attempted to defend itself by saying the plant was only built to provide occasional backup and insurance for Kabul’s electrical grid, not for electrical power on a continuous basis. SIGAR’s report provides evidence that the plant was built for regular usage.
Related: U.S. Military Builds a $15 Million Warehouse That Nobody Wants
First, the basis of design was for a base load plant, built to operate 24 hours per day, 7 days a week. Also, the plant hasn’t made any impact on reducing Kabul’s massive energy deficit that USAID says is one of the plant’s main priorities. Not only is it not being used regularly, but it’s not even contributing additional electricity to increase the overall power supply in Kabul.
The Tarakhil Power Plant was built in July 2007 on the outskirts of Kabul, with the intention of supplying 18 diesel engines worth of operating power. Since Da Afghanistan Breshna Sherkat (DABS) – Afghanistan’s national power utility – assumed responsibility for the operation and maintenance of the facility in 2010, the plant has only performed at a shred of its total capability. Between July 2010 and December 2013, the USAID IG found that the plant performed at a mere 2.2 percent of its potential.
Since the Tarakhil Power Plant was used incorrectly and only on an intermittent basis, the plant has suffered premature wear and tear on its engine and electrical components. The damage is expected to raise already steep operation and maintenance costs.
How Good Is Your Insurance? ‘Cadillac Tax’ Looms for Large Employer Health Plans

While most companies expect health care cost increases to hold steady next year, nearly half of large employers say that if they can’t find new ways to cut costs, they’re going to cross the “Cadillac tax” threshold in 2018, according to a new study by the National Business Group on Health.
Passed as part of the Affordable Care Act and going into effect in 2018, the Cadillac tax will hit employers whose plans cost more than $10,200 for an individual or $27,500 for a family. The employer will have to pay a 40 percent tax on the cost of each plan above those levels.
Among the companies surveyed, 48 percent said that at least one of their benefit plans would trigger the Cadillac Tax. By 2020, 72 percent of employers say one of their plans will trigger the tax, and 51 percent say their most popular plan will be subject to the tax.
Related: Obamacare’s Cadillac Tax Hits the College Campus
“The need to control rising health care benefits costs has never been greater,” NGBH President and CEO Brian Marcotte said in a statement. “Rising costs have plagued employers for many years and now the looming excise tax is adding pressure.”
Employers expect keep benefit costs increases to 5 percent this year by pushing more costs onto workers via consumer-directed health plans (76 percent) and expanding wellness initiatives (70 percent).
None of the 425 employers surveyed said they planned to eliminate their health care coverage, but nearly a quarter said they’d consider offering employees a private exchange.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- How ‘King Coal’ Could Swing the 2016 Election
- Kerry to Congress: Sign the Iran Deal or the Dollar Gets Hit
- China’s Currency Devaluation Brings Stocks to a 'Death Cross'